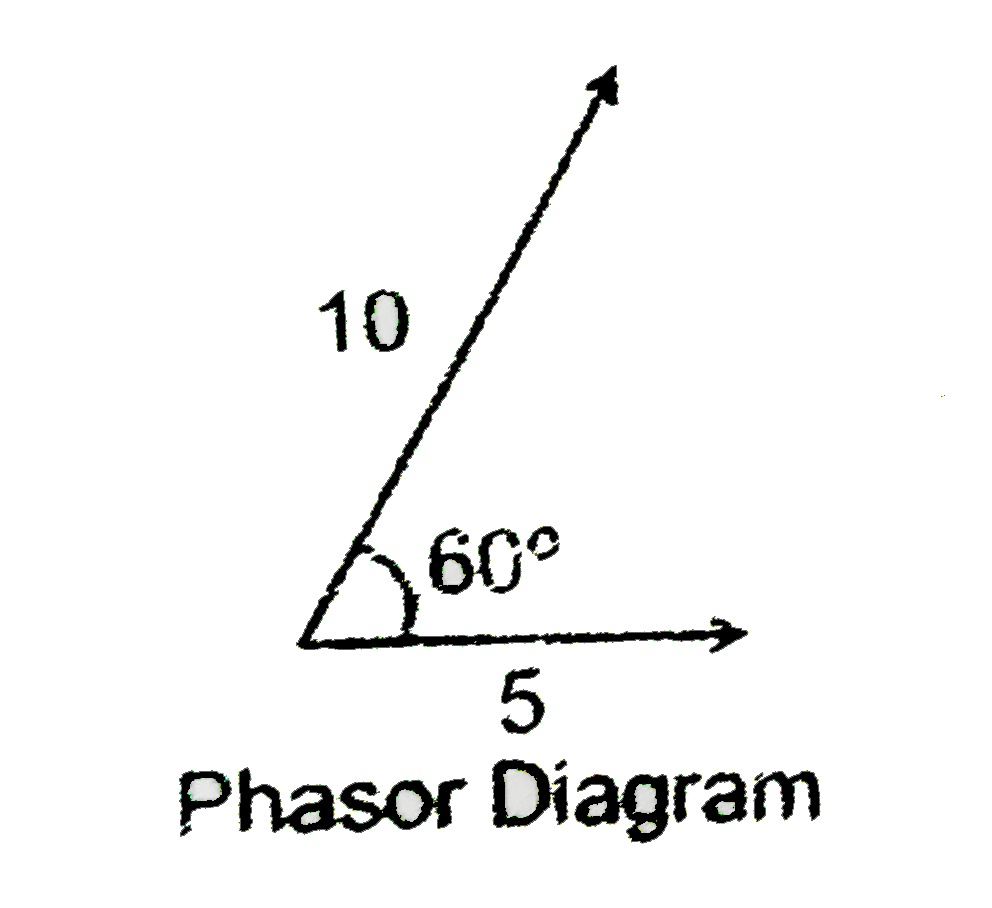Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION -Advanced Level Problems
- x(1) = 5 sin (omegat + 30^(@)) x(2) = 10 cos (omegat) Find amplitu...
Text Solution
|
- What would be the period of the free oscillations of the system shown ...
Text Solution
|
- A constant force produces maximum velocity V on the block connected to...
Text Solution
|
- Two point masses m(1) and m(2) are fixed to a light rod hinged at one ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere of (radius = R) rolls without slipping in a cylindrical...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m in suspended at the lower end of a thin negligibl...
Text Solution
|
- If velocity of a partical moving along a straight line changes sinuso...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles P(1) and P(2) are performing SHM along the same line abo...
Text Solution
|
- Two simple pendulums A and B having lengths l and (l)/(4) respectively...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 'm' is moving in the x-y plane such that its x and ...
Text Solution
|
- Two non - viscous, incompressible and immiscible liquids of densities ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical balls A and B each of mass 0.1 kg are attached to two id...
Text Solution
|
- Two light spring of force constants k(1) and k(2) and a block of mass ...
Text Solution
|
- Two wheels which are rotated by some external source with constant ang...
Text Solution
|