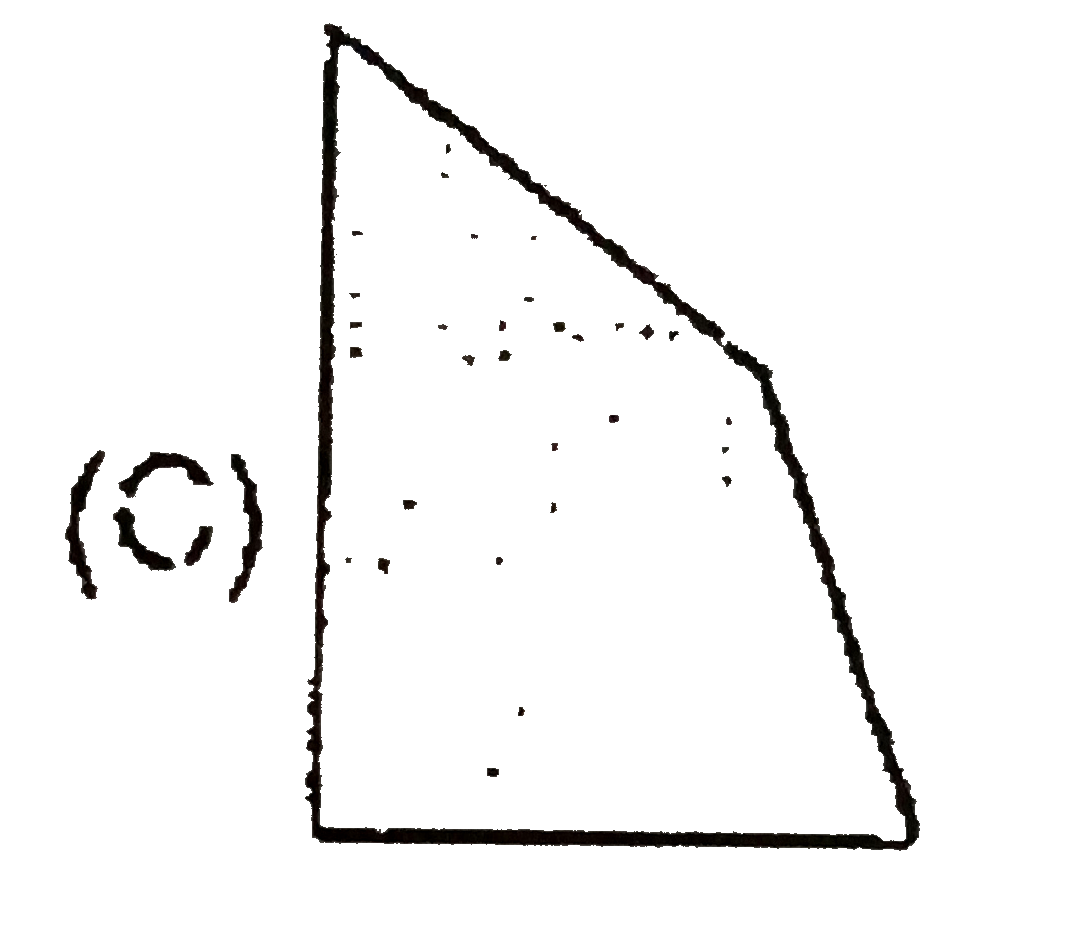
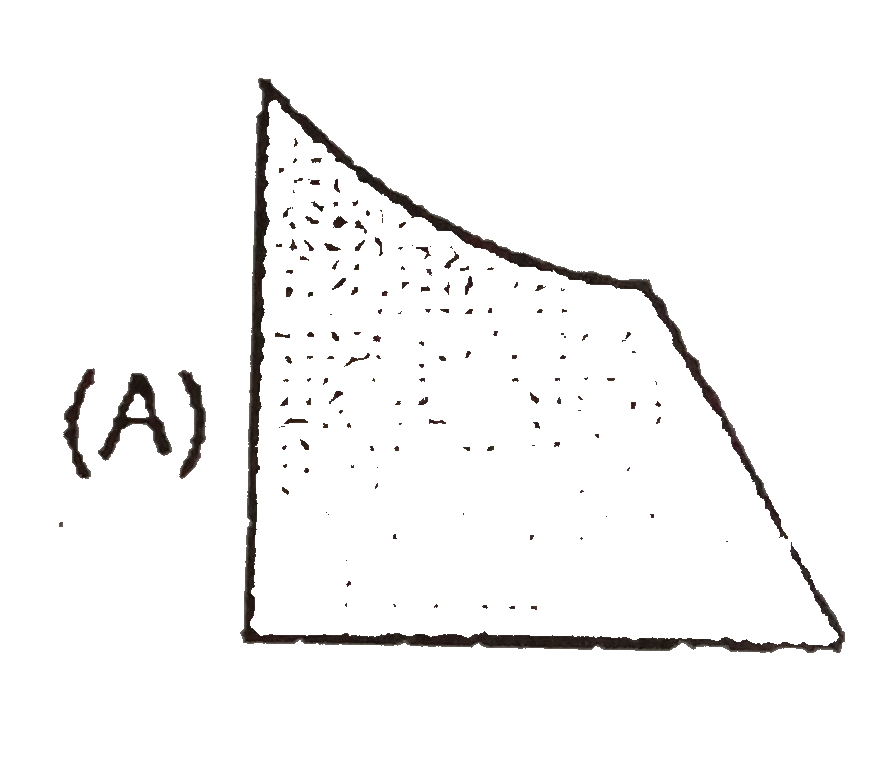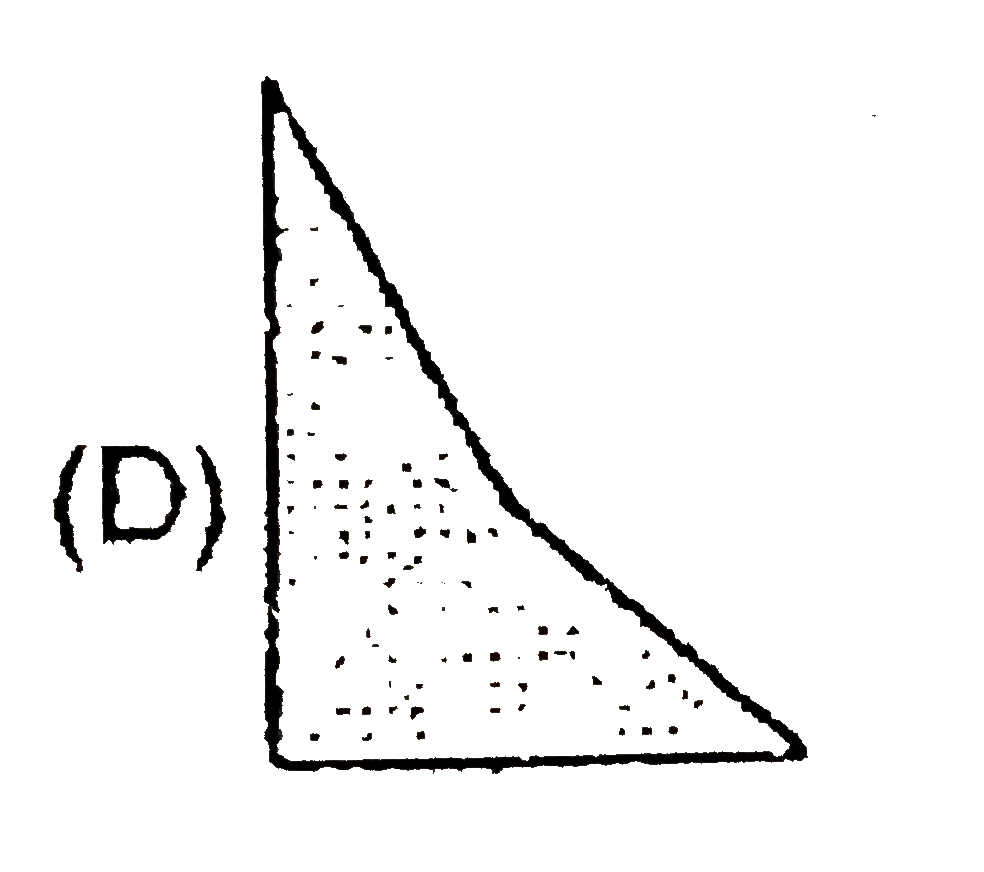A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VIBRANT-REVIEW TEST-PART - II : PHYSICS
- Mark the correct statements:
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows position-time graph of two cars A and B.
Text Solution
|
- A football is rolling down a hill of unknown shape. The speed of the f...
Text Solution
|
- The following figure shows the velocity time graph of a body. Accordin...
Text Solution
|
- The acceleration (a) of moving particle varies with displacement accor...
Text Solution
|
- The initial velocity of a particle is u (at t = 0) and the acceleratio...
Text Solution
|
- Two projectiles are thrown simultaneously in the same plane from the s...
Text Solution
|
- Two projectivles are thrown simultaneously in the same plane from the ...
Text Solution
|
- At t=0 a projectile is fired from a point O (taken as origin) on the g...
Text Solution
|
- At t=0 a projectile is fired from a point O (taken as origin) on the g...
Text Solution
|
- A body is projected at an angle 60^(@) with the horizontal ground with...
Text Solution
|
- A rod can freely rotate in vertical plane about a hinge at its bottom....
Text Solution
|
- A bus is moving on a horizontal road with speed 5m//s. A & B are two p...
Text Solution
|
- A pendulum of mass m and length l [ as in figure] is attached to the t...
Text Solution
|
- A snail boat sails 2 km due East, 5 km 37^(@) South of East and finall...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass M sits on an inclined plane and is connected via a mas...
Text Solution
|
- An electric sander has a continuous belt that rubs against a wooden su...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 1 kg start moving at t = 0 with speed 2 m//s on rough ...
Text Solution
|
- Assume that all the pulleys are massless and frictionless and strings ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m(1) lies on top of fixed wedge as shown in figure 1 a...
Text Solution
|