A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VIBRANT-REVIEW TEST-PART - II : PHYSICS
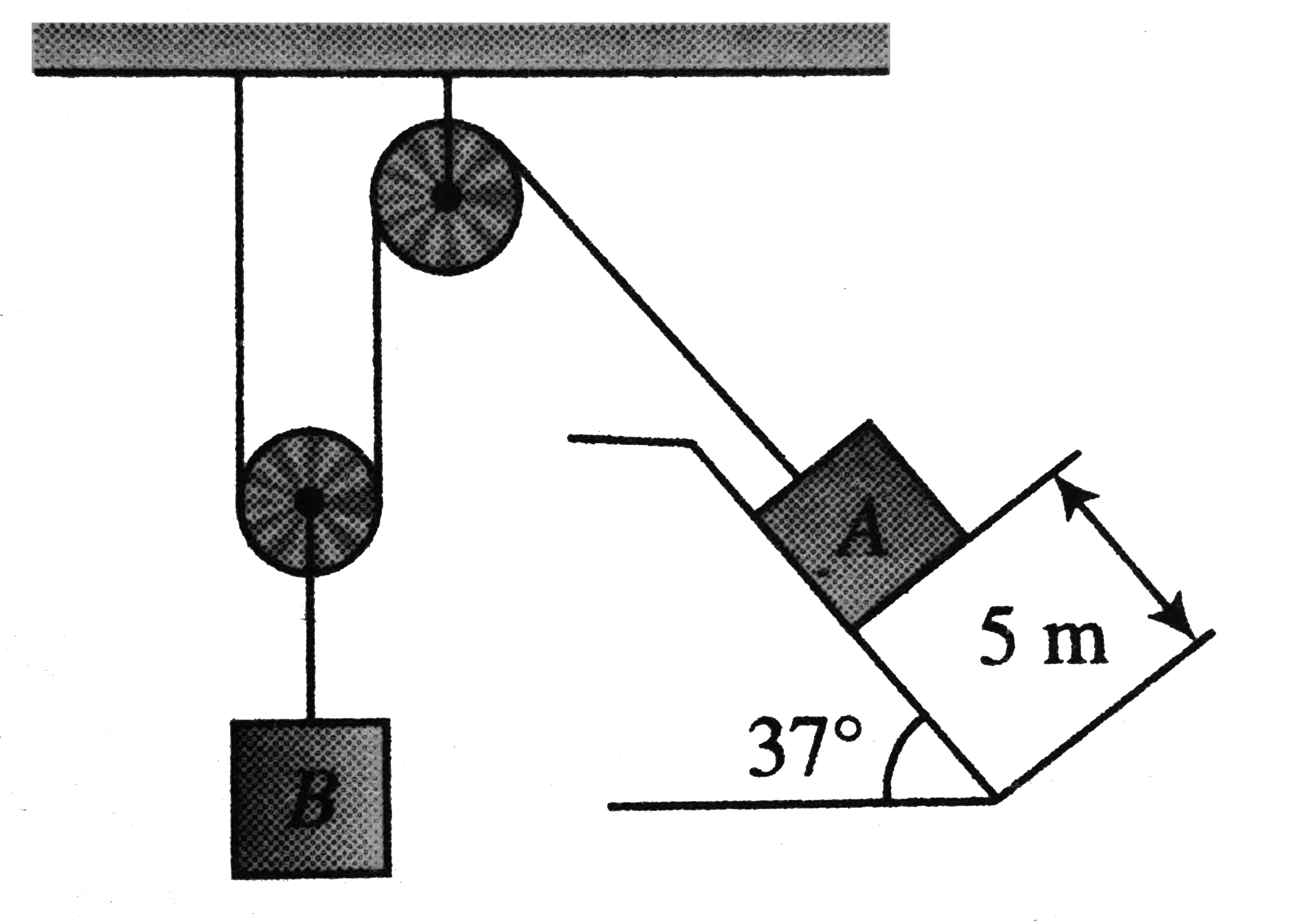
- The blocks A and B shown in figure have masses MA=5kg and MB=4kg. The ...
Text Solution
|
- In (x-y) plane motion of particle it's (x-y) coordinate depends on tim...
Text Solution
|
- Three forces of magnitude 10N are acting on a block of mass 2 kg at 12...
Text Solution
|
- Find int(0)^(1)picos((pi)/(2)t)dt=?
Text Solution
|
- During displacement of a body two forces are acting on it simultaneous...
Text Solution
|
- Resultant of two forces when angle between them is 60^(@) is 6 Newton ...
Text Solution
|
- Force vec(F)=(4sqrt(2hat(i))+3sqrt(2)hat(j)) acting on a body so that ...
Text Solution
|
- Two forces 10 N and 15 N are acting on a body then which cannot be the...
Text Solution
|
- If acceleration of particle changing with time is a = (4t-2) m//s^(2) ...
Text Solution
|
- Young modulus of steel is 3 xx 10^(11) N//m^(2). When expressed in C.G...
Text Solution
|
- If momentum P, area A and time T are selected as fundamental quantitie...
Text Solution
|
- Two forces are acting on body vec(F)(1)=-(50-t^(2))hat(j) Newton and v...
Text Solution
|
- In the given velocity v//s position graph find acceleration at x = 2m
Text Solution
|
- Select correct statements
Text Solution
|
- If x = (4t^(2)+2) any y = 2t, then find ((dx)/(dy)) at t = 2 sec. (x i...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following cannot be the group of fundamental quantities. ...
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1 : Using dimensional analysis we can drive only those formu...
Text Solution
|
- If side length of cube changing at 0.1mm//sec. Then what will be rate ...
Text Solution
|
- During one dimensional motion on x-axis Velocity time graph for partic...
Text Solution
|
- During one dimensional motion on x-axis Velocity time graph for partic...
Text Solution
|
- During one dimensional motion on x-axis Velocity time graph for partic...
Text Solution
|