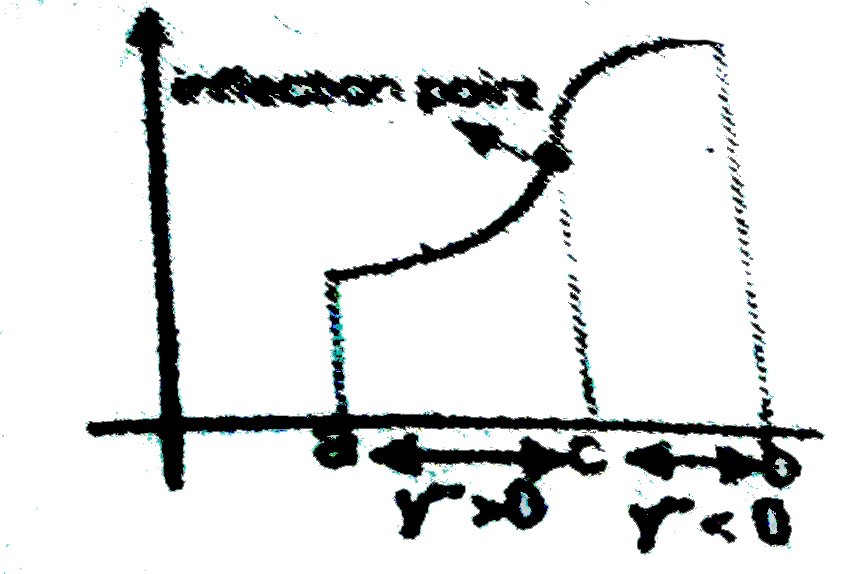A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
APPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES
RESONANCE|Exercise Exersise-3 Part I|27 VideosAPPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES
RESONANCE|Exercise Exersise-3 Part II|22 VideosAPPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES
RESONANCE|Exercise Exersise-2 Part III|23 VideosCOMBINATORICS
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise-2 (Part-II: Previously Asked Question of RMO)|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-APPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES-Exersise-2 Part IV comprehension
- Let P (h,K) be any point on curve y=f(x). Let tangent drawn at p...
Text Solution
|
- Let P (h,K) be any point on curve y=f(x). Let tangent drawn at p...
Text Solution
|
- Let P (h,K) be any point on curve y=f(x). Let tangent drawn at p...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a function f defined by f(x)=sin^(-1) sin ((x+sinx)/2) AA x i...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a function f defined by f(x)=sin^(-1) sin ((x+sinx)/2) AA x i...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a function f defined by f(x)=sin^(-1) sin ((x+sinx)/2) AA x i...
Text Solution
|
- Concavity and convexity : if f''(x) gt 0 AA x in (a,b) then the c...
Text Solution
|
- Concavity and convexity : if f''(x) gt 0 AA x in (a,b) then the c...
Text Solution
|
- For a double diferentiable function f(x) if f''(x) ge 0 then f(x) ...
Text Solution
|
- For a double diferentiable function f(x) if f''(x) ge 0 then f(x) ...
Text Solution
|
- For a double diferentiable function f(x) if f''(x) ge 0 then f(x) ...
Text Solution
|