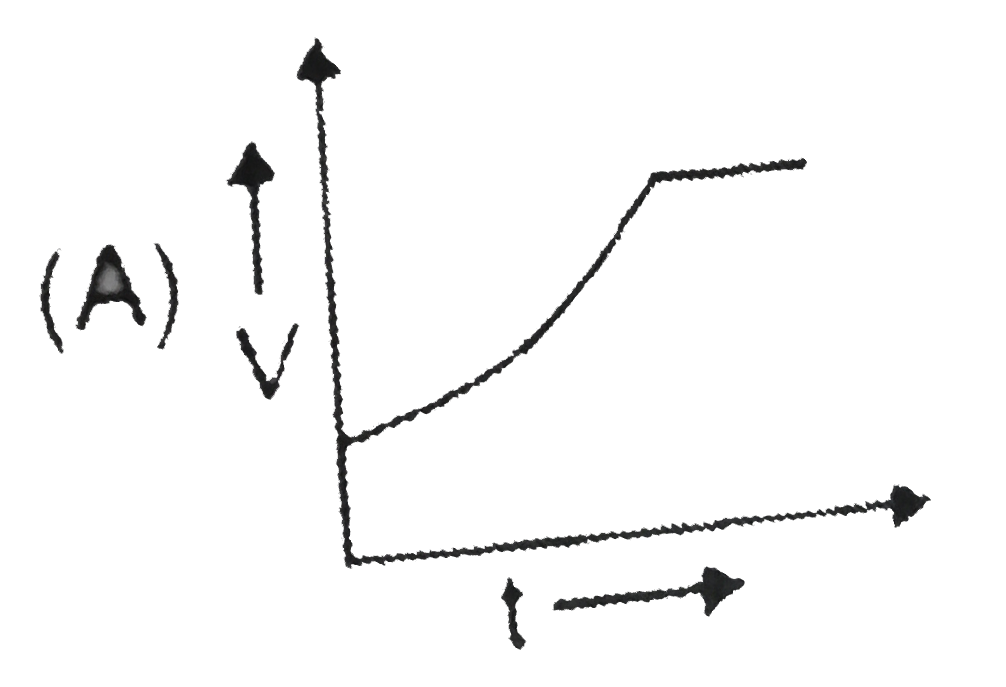
A
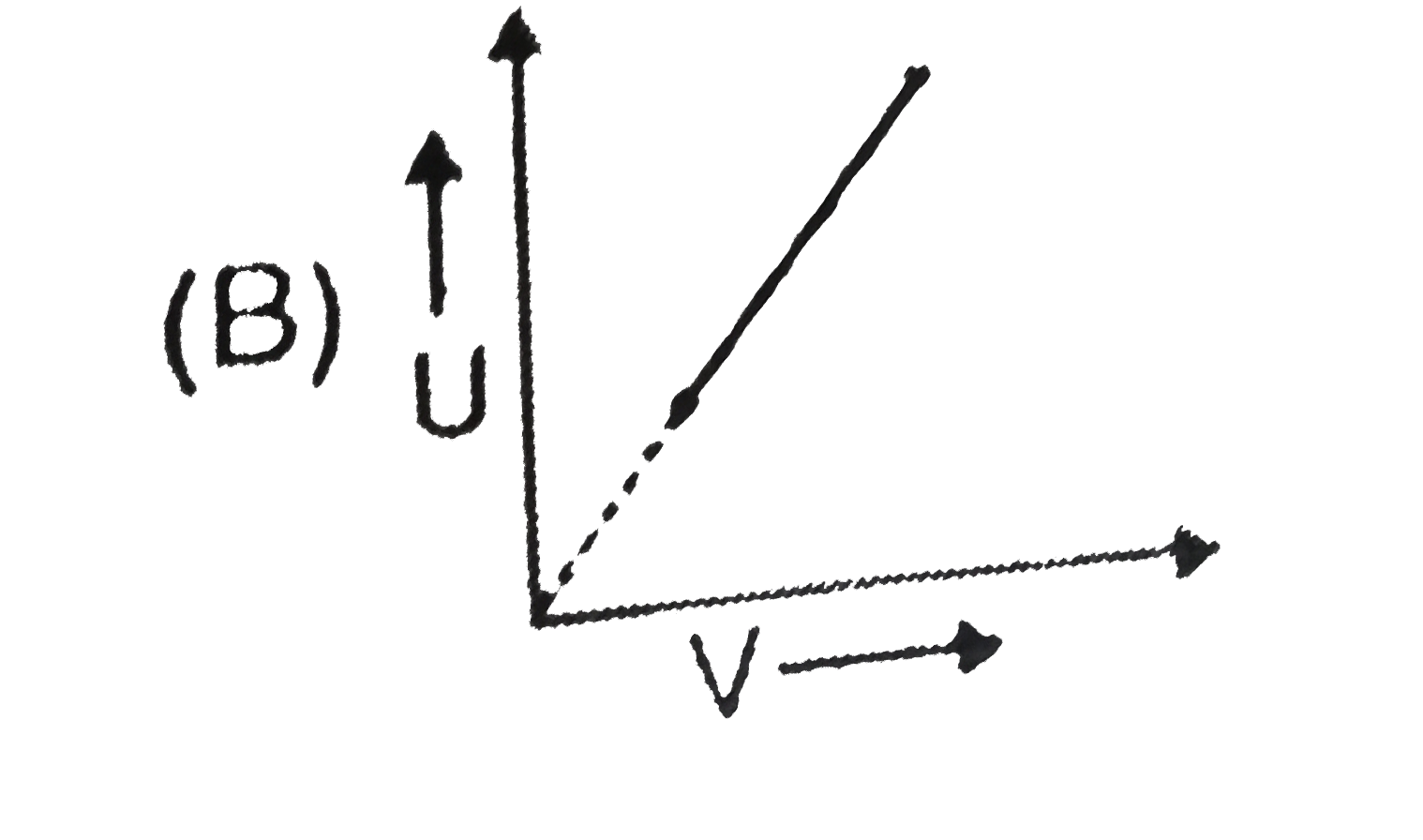
B
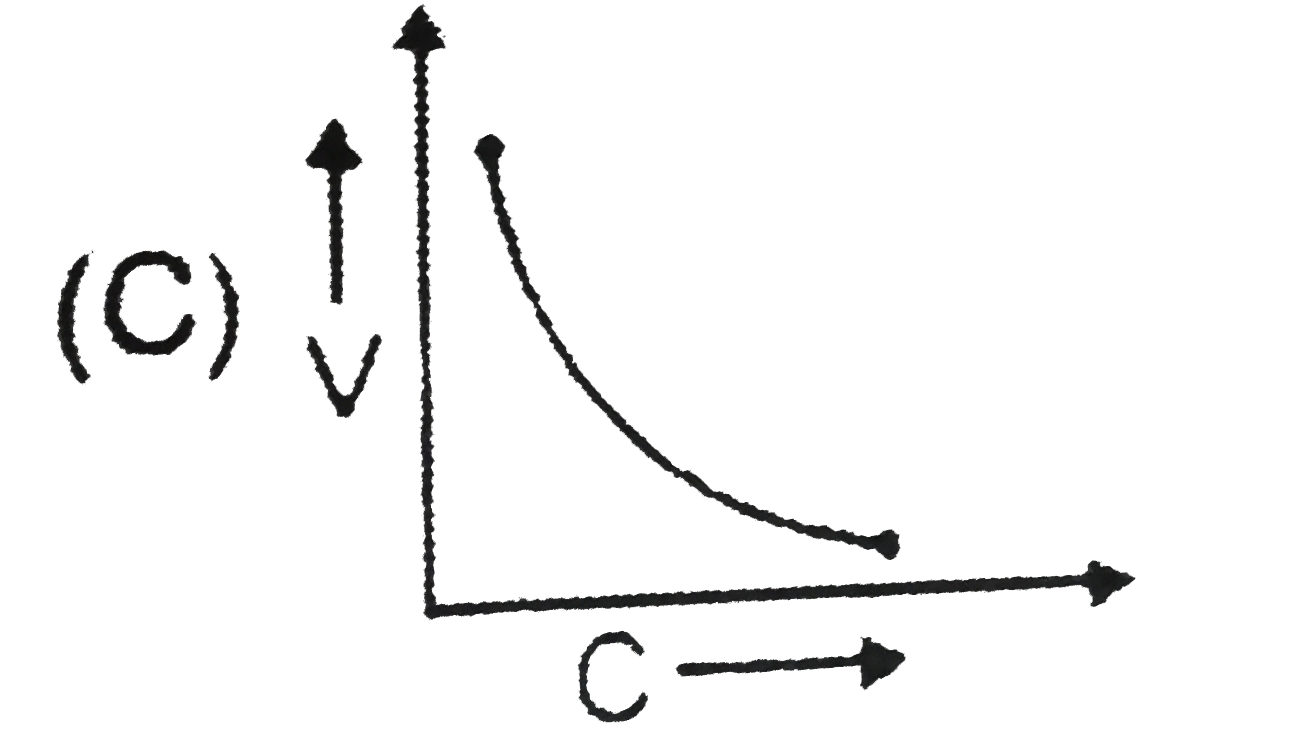
C
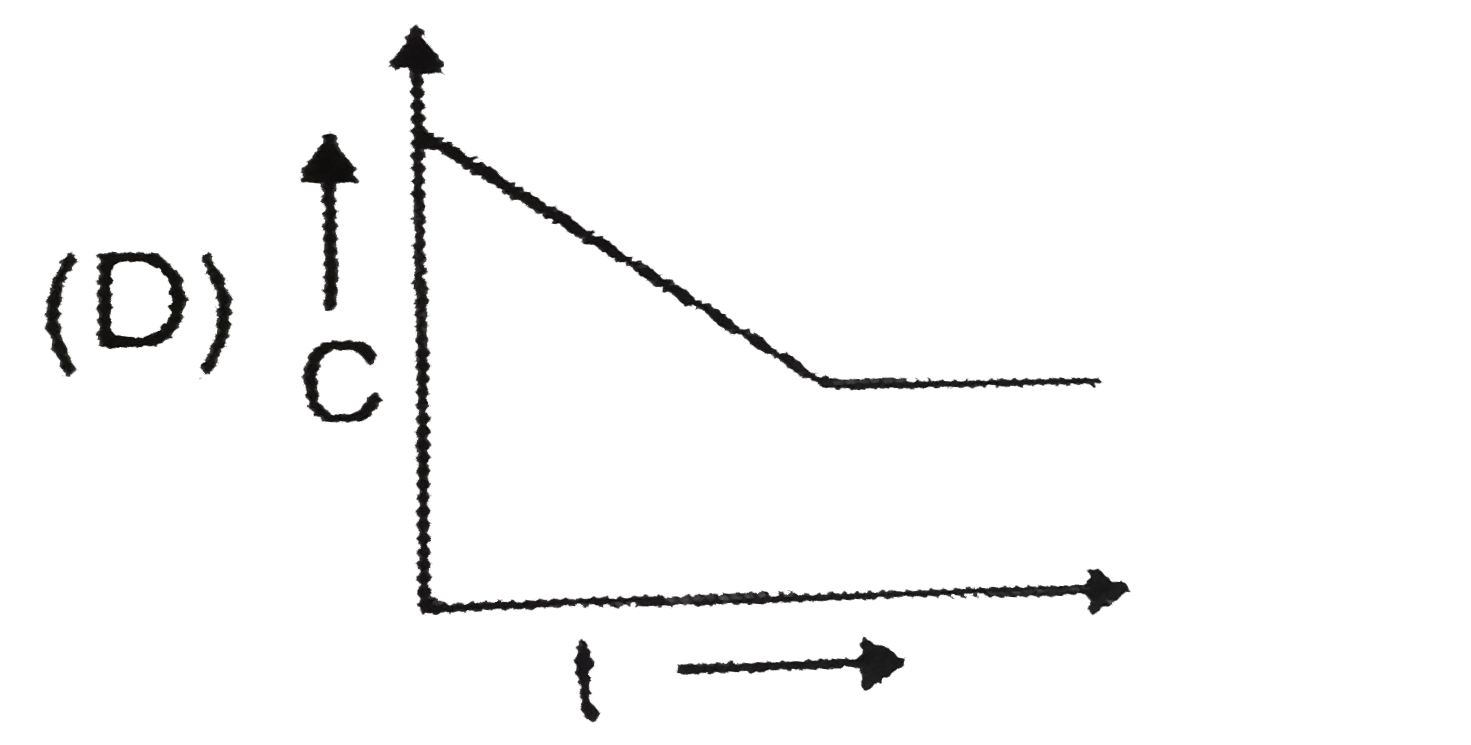
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-CAPACITANCE-Exercise - 2
- In the adjoining diagram all the capacitors are initially uncharged, ...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in figure the switch S is closed at t = 0. A lo...
Text Solution
|
- When a charged capacitor is connected with an uncharged capacitor , t...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown each capacitor has a capcitance C. The emf of the...
Text Solution
|
- Two similar condensers are connected in parallel and are charged to...
Text Solution
|
- We have a combination as shown in following figure. Choose the corre...
Text Solution
|
- The charge across the capacitor in two different RC circuit 1 and 2 ar...
Text Solution
|
- The instantaneous charge on capacitor in two discharging RC circuils...
Text Solution
|
- Capacitor C1 of capacitance 1 micro-farad and capacitor C2 of capacita...
Text Solution
|
- The terminals of a battery of emf V are connected to the two plates of...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel plate capacitor of plate area A and plate separation d is c...
Text Solution
|
- The plates of a parallel plate capacitor with no dielectirc are connec...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel plate capacitor has a dielectric slab in it. The slab jus...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel plate air capacitor is connected to a battery. The quantiti...
Text Solution
|
- Capacitor C(3) in the circuit is a veriable capacitor (its capacitance...
Text Solution
|
- Capacitor C(3) in the circuit is a veriable capacitor (its capacitance...
Text Solution
|
- Capacitor C(3) in the circuit is a veriable capacitor (its capacitance...
Text Solution
|
- In the shown circuit involving a resistor of resistance R Omega, capa...
Text Solution
|
- In the shown circuit involving a resistor of resistance R Omega, capa...
Text Solution
|
- In the shown circuit involving a resistor of resistance R Omega, capa...
Text Solution
|