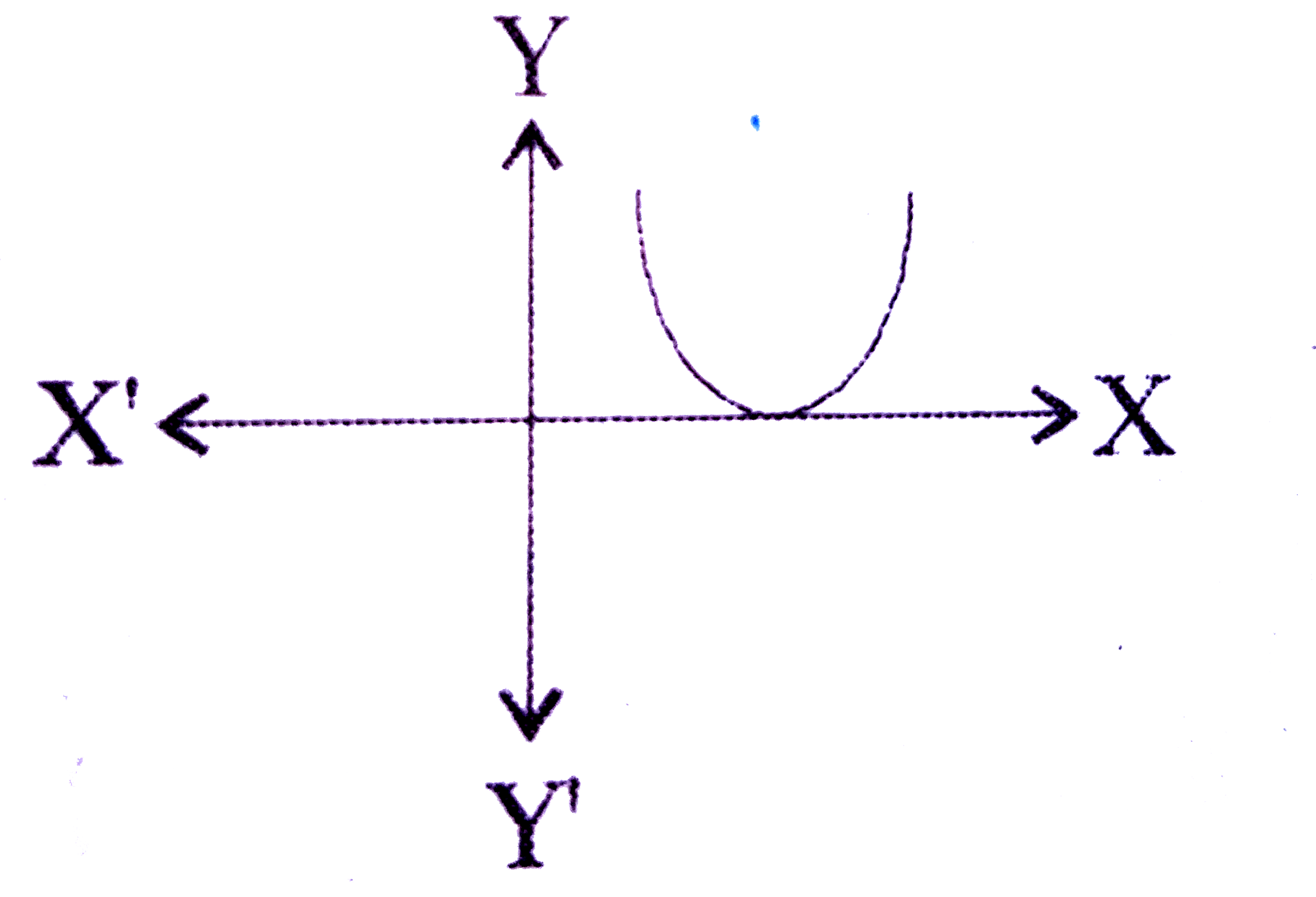
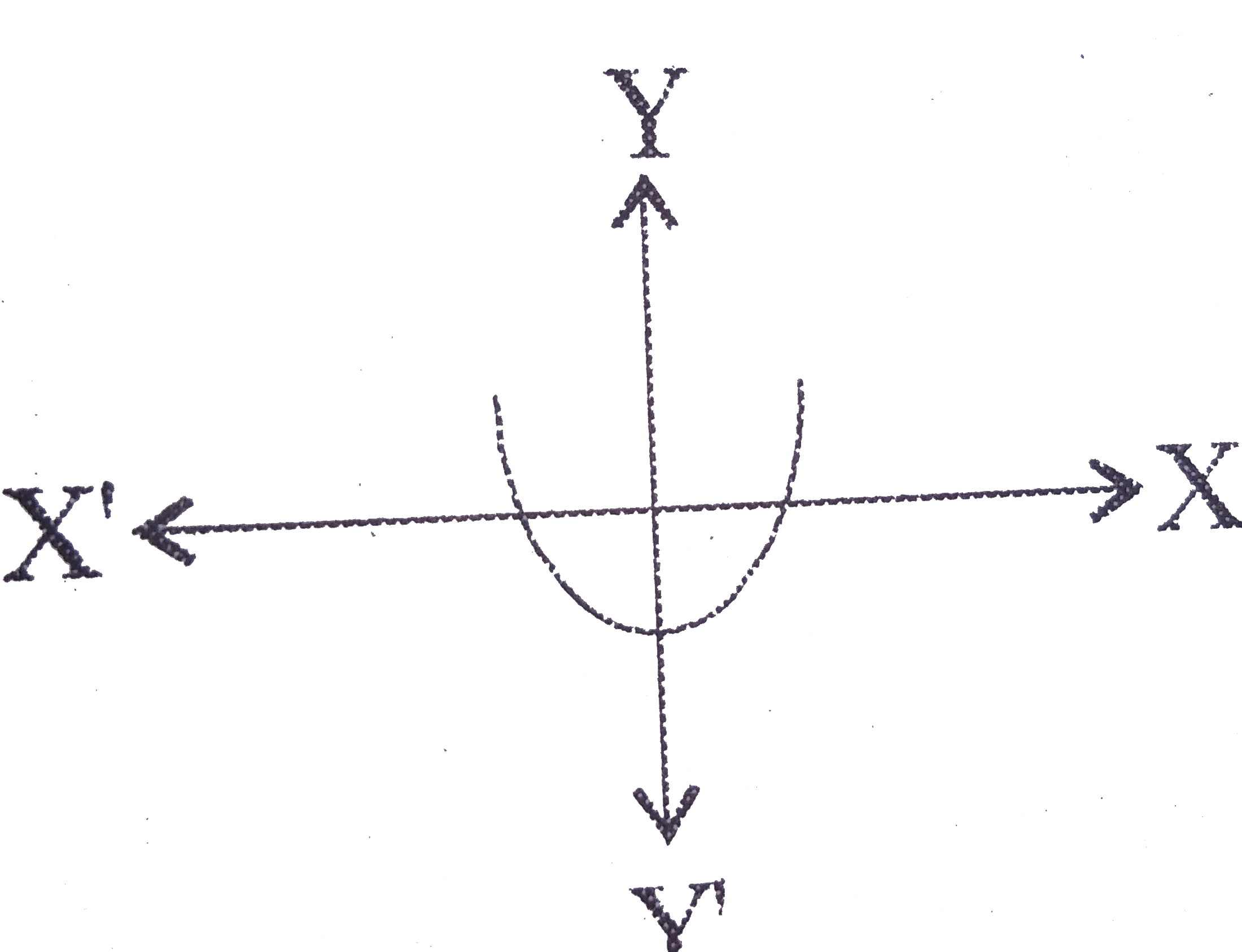
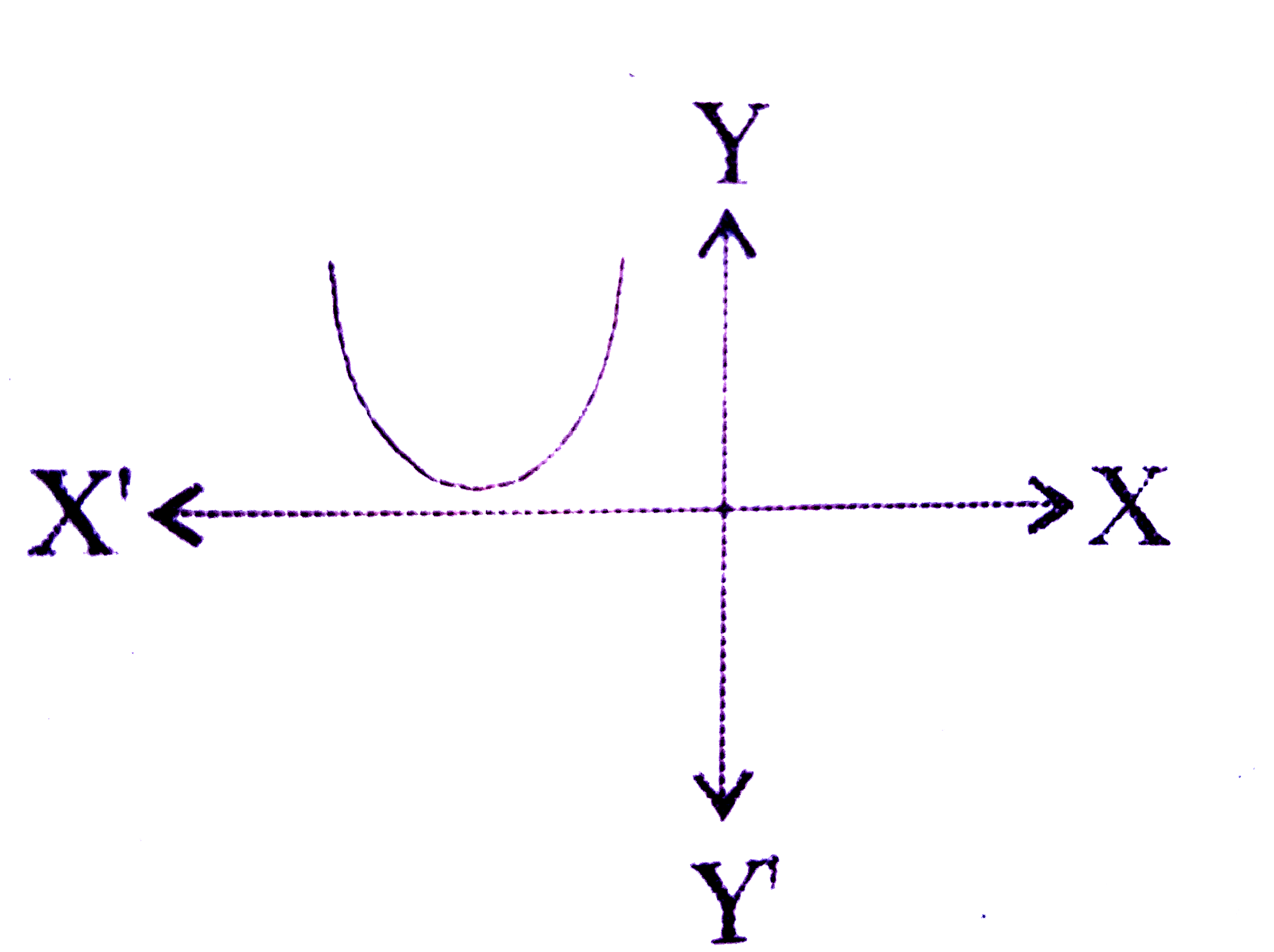
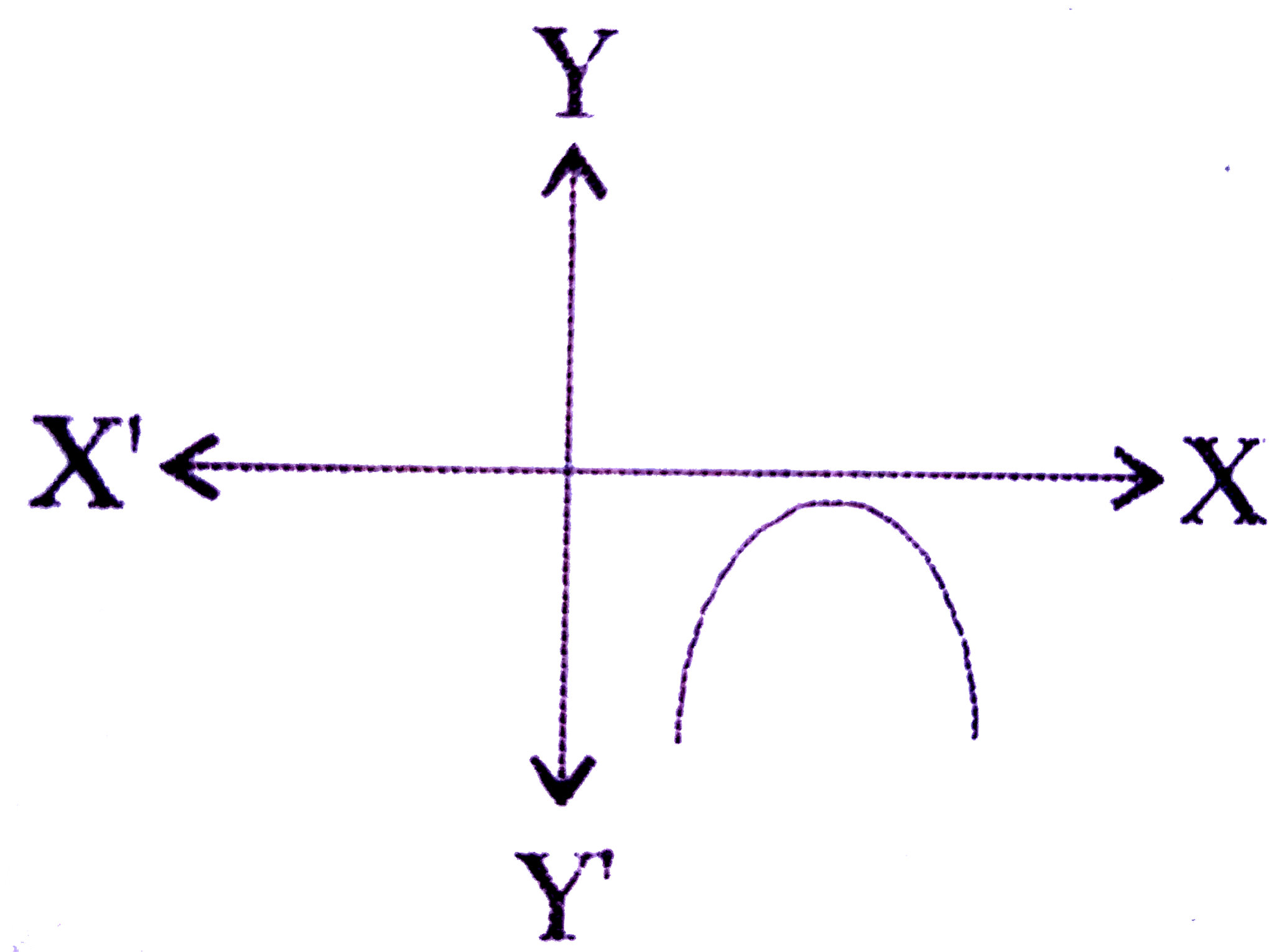
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
QUADRATIC EQUATIONS
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise CREATIVE BITS FOR CCE MODEL EXAMINATION|130 VideosQUADRATIC EQUATIONS
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise EXERCISE|270 VideosQUADRATIC EQUATIONS
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise OBSERVATION MATERIAL TO SOLVE VARIOUS QUESTIONS GIVEN IN THE PUBLIC EXAMINATION|22 VideosPROGRESSIONS (MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION)
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise PROGRESSIONS (MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION)|20 VideosQUADRATIC EQUATIONS (MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION)
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise QUADRATIC EQUATIONS (MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION)|20 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT-QUADRATIC EQUATIONS-OBSERVATION BITS TO SOLVE VARIOUS BITS GIVEN IN THE PUBLIC EXAMINATION
- The adjacent diagram indicates…..
Text Solution
|
- If alpha, beta "are the roots of" x^(2) - 10x + 9 =0, "then" |alpha - ...
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following figures shows the quadratic equation ax^(2)...
Text Solution
|
- If 1 is a common root of ax^(2) + ax + 2 = 0 and x^(2) + x + b = 0 "th...
Text Solution
|
- The number of diagonals for an n sided polygon is
Text Solution
|
- A quadratic equation ax^(2) + bx + c = 0 has two distinct real roots, ...
Text Solution
|
- The discriminant of the quadratic equation px^(2) + qx + r = 0 is….
Text Solution
|
- The discriminant of 6x^(2) - 5x + 1 = 0 "is"
Text Solution
|
- One root of the equation x-3/x=2 is……….
Text Solution
|
- The quadratic polynomial, whose zeroes are sqrt 2 and -sqrt2 is
Text Solution
|
- If the equation x^(2) + 5x + K = 0 has real and distinct roots, then….
Text Solution
|
- The quadratic polynomial, whose zeros are 2 and 3, is…..
Text Solution
|
- Observe the given rectangular figure, then its area in polynomial func...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is a quadratic equation?
Text Solution
|
- Observe the following graphs. Which as them are the graphs of q...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following quadratle. Equations the roots are equal?
Text Solution
|
- The quadratic polynomial having 1/3 and 1/2 as its zeroes, is…..
Text Solution
|
- If x^(2) - px + q = 0 (p,q in R and p ne 0, q ne 0) has distinct real ...
Text Solution
|
- In a quadratic equation ax^(2) + bx + c = 0 "if" b^(2) - 4ac gt 0 then...
Text Solution
|
- If a number is 132 smaller than its square, then the number is
Text Solution
|