Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE-COORDINATE SYSYEM -JEE Main Previous Year
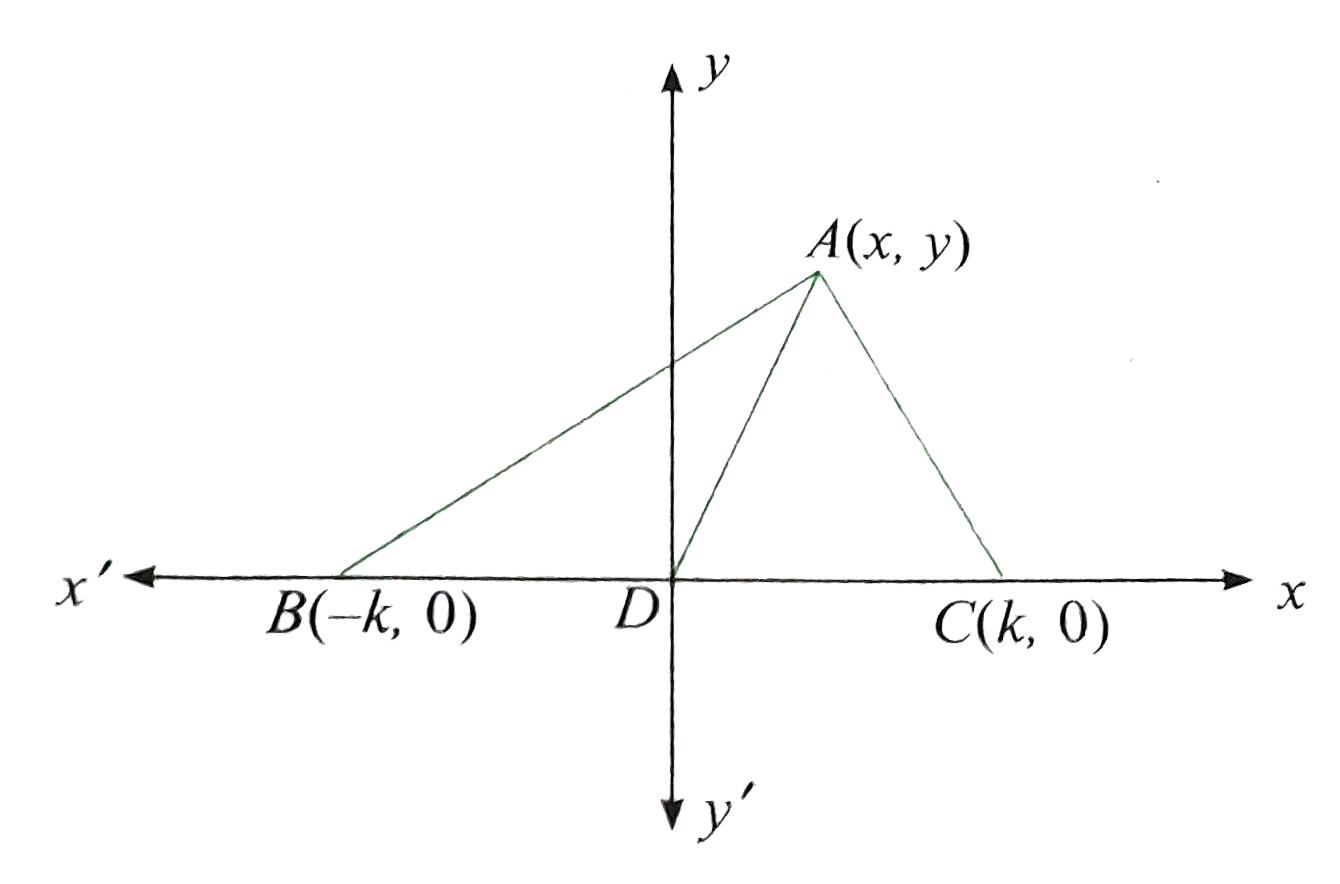
- In any triangle ABC, prove that AB^2 + AC^2 = 2(AD^2 + BD^2) , where D...
Text Solution
|
- The lines p(p^2+1)x-y+q=0 and (p^2+1)^2x+(p^2+1)y+2q=0 are perpendicul...
Text Solution
|
- If the line 2x + y = k passes through the point which divides the line...
Text Solution
|
- The number of points, having both co-ordinates as integers, that lie i...
Text Solution
|
- Let k be an integer such that the triangle with vertices (k ,-3k),(...
Text Solution
|
- Let the orthocentre and centroid of a triangle be (-3,5) and B(3,3) r...
Text Solution
|
- The straight line through a fixed point (2,3) intersects the coordinat...
Text Solution
|