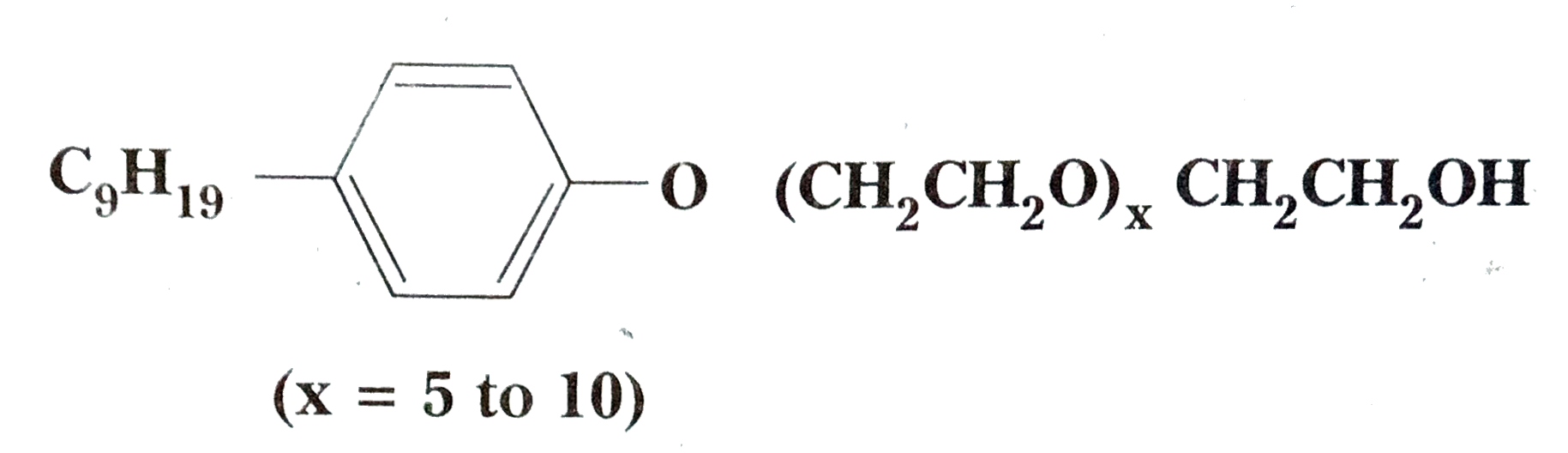Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT TELUGU-CHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFE-Exercises
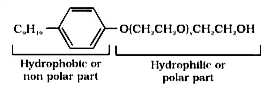
- Following type of non-ionic detergents are present in liquid detergent...
Text Solution
|
- Why do we need to classify the drug in different ways?
Text Solution
|
- Explain the term target molecules or drug targets as used in medicinal...
Text Solution
|
- Name the marcomolecules that are chosen as drug targets.
Text Solution
|
- Why should not medicines be taken without consulting doctors ?
Text Solution
|
- Define the term chemotherapy.
Text Solution
|
- Which forces are involved in holding the drug to the drug to active si...
Text Solution
|
- While antacids and antiallergic drugs interface with the function of h...
Text Solution
|
- Low level of noradrenaline in the cause of depression.What type of dru...
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by the term broad spectrum antibiotics?Explain.
Text Solution
|
- How do antiseptics differ from disinfectants?Does the same substance b...
Text Solution
|
- Why are cimetidine and ranitidine better antacids than sodium hydrogen...
Text Solution
|
- Name a substance which can be used as an antiseptic as well disindecta...
Text Solution
|
- What are the main constituents of dettol?
Text Solution
|
- What is tincture of iodine?What is its use?
Text Solution
|
- What are food predervatives?Give example.
Text Solution
|
- Why is the use if aspartame limited to cold foods and drinks?
Text Solution
|
- What are artificail sweerening agents?Give example.
Text Solution
|
- Name the sweetening agent used in the prepration of seets for a diabet...
Text Solution
|
- What problem does arise in using alitame as artificial sweetener?
Text Solution
|
- How are synthetic detergents better than soaps?
Text Solution
|