Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-LAW OF MOTION-EXERCISE - IV
- All surfaces are smooth Find the horizontal displacements of the block...
Text Solution
|
- When a body is stationary:
Text Solution
|
- The inertia of a moving object depends on:
Text Solution
|
- A thief stole a box full of valuable articles of weight W and while ca...
Text Solution
|
- There are three Newton's laws of motion namely I, II and III : we can ...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks m(1) = 5 g and m(2)= 10 g are hung vertically over a light ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure a smooth pulley of negligible weight is suspended by a s...
Text Solution
|
- Two masses 2 kg and 3 kg are attached to the end of the string passed ...
Text Solution
|
- Two bodies of mass 6 kg and 4 kg are tied to a string as shown in the ...
Text Solution
|
- The pulley arrangements shown in figure are identical, the mass of the...
Text Solution
|
- A string of negligible mass going over a clamped pulley of mass m supp...
Text Solution
|
- Two masses of 8 kg and 4 kg are connected by a string as shown in figu...
Text Solution
|
- An empty plastic box of mass m is found to accelerate up at the rate o...
Text Solution
|
- A monkey is decending from the branch of a tree with constant accelera...
Text Solution
|
- Fig. shows a system of three masses being pulled with a force F. the m...
Text Solution
|
- Fig. shows a block of mass m(1) resting on a smooth surface. It is con...
Text Solution
|
- A 100 kg block is suspended with the help of three strings A, B and C....
Text Solution
|
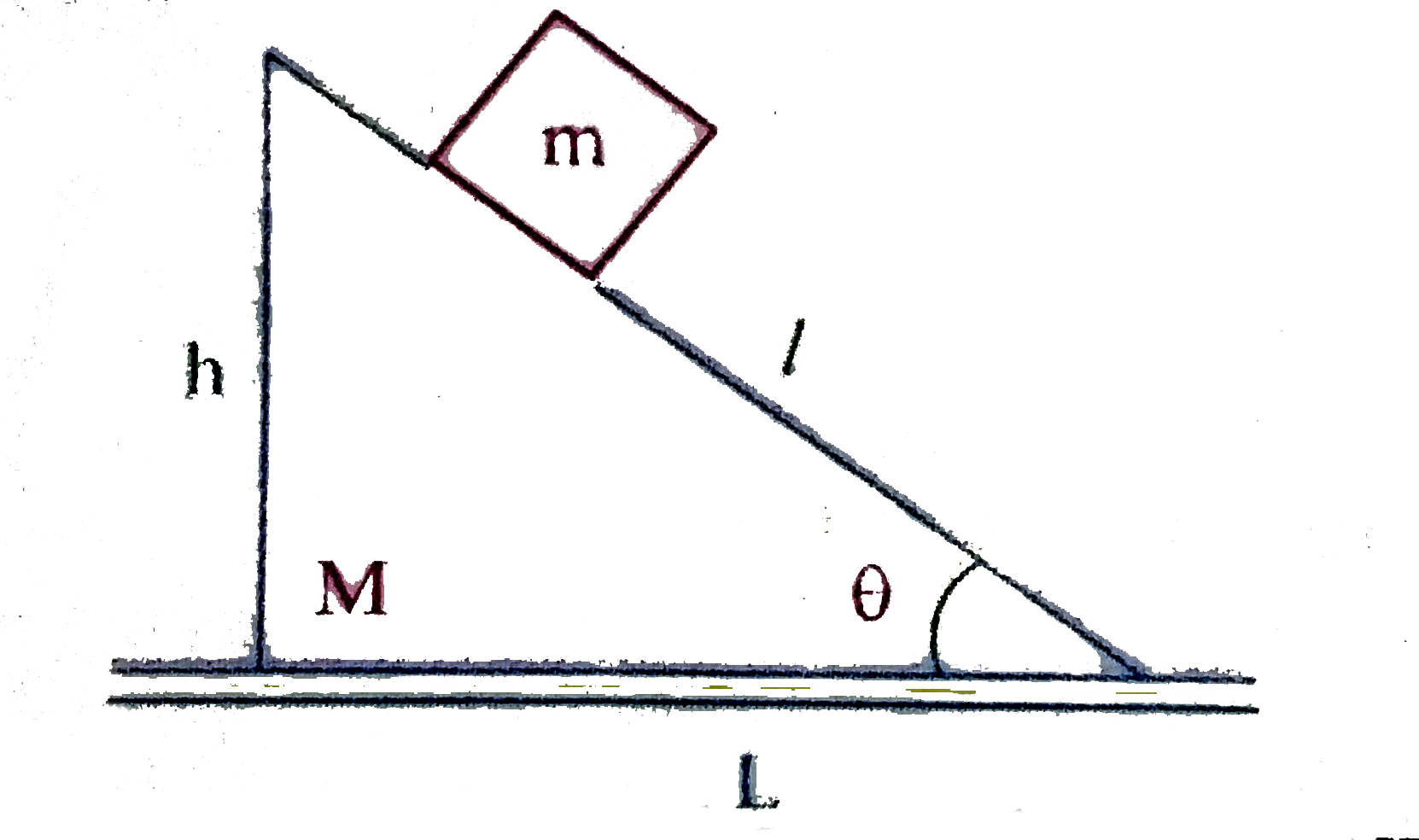
- A frictionless inclined plane of length l having inclination theta is ...
Text Solution
|
- Friction
Text Solution
|
- A box is placed on an inclined plane and has to be pushed down.The ang...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows two block A and B pushed against the wall with the force ...
Text Solution
|
 .
.