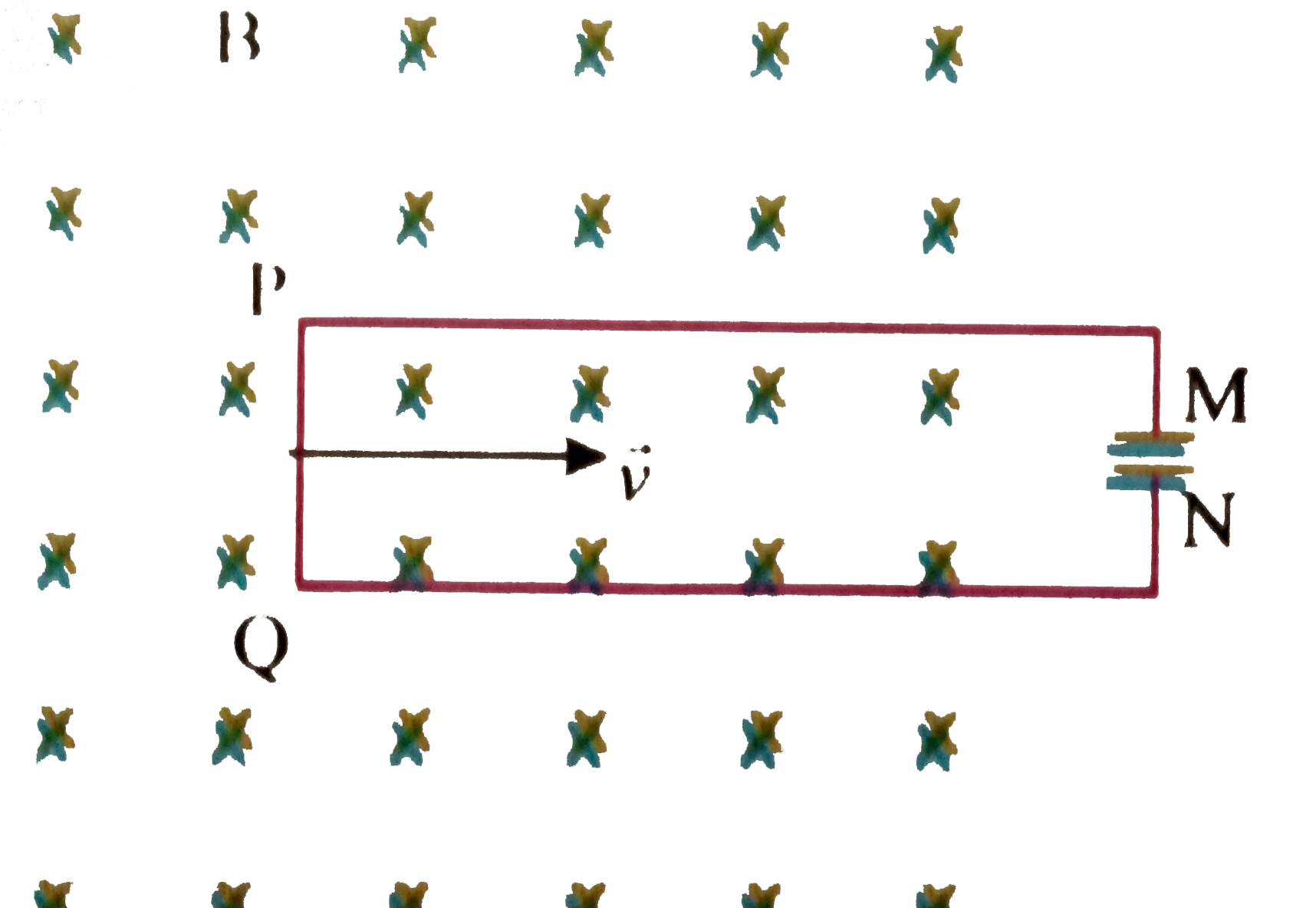
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
NARAYNA|Exercise EXERCISE-2 (H.W)|16 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
NARAYNA|Exercise EXERCISE-3|24 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
NARAYNA|Exercise EXERCISE-1 (H.W)|43 VideosELECTRO MAGNETIC WAVES
NARAYNA|Exercise LEVEL-II(H.W)|14 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
NARAYNA|Exercise EXERCISE -4|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-EXERCISE-2 (C.W)
- a physicist works in a laboratory where the magnetic field is 2T. She ...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel rails of a railway track insulated from each other and wi...
Text Solution
|
- A rod PQ is connected to the capacitor plates. The rod is placed in a ...
Text Solution
|
- A wire is sliding as shown in Figure. The angle between the accelerati...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting wire xy of lentgh l and mass m is sliding without frictio...
Text Solution
|
- A conducitng rod AB of length l = 1 m moving at a velcity v = 4 m//s m...
Text Solution
|
- A wire KMN moves along the bisector of the angle theta with a constant...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform magnetic field existsin region given by vec(B) = 3 hat(i) + ...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod PQ of length 1 m is moving with uniform velocity of 2...
Text Solution
|
- A time varying magnetic field is present in a cyclindrical region R as...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic square loop ABCD is moving in its own plane with velocity v...
Text Solution
|
- The flux linked with a coil is 0.8 Wb when a 2 A current is flowing th...
Text Solution
|
- A solenoid of self inductance 1.2 H is in series with a tangent galvan...
Text Solution
|
- There are two batteries 'A' and 'B' having same emf. A has no internal...
Text Solution
|
- An emf induced in a secondary coil is 10000 V when the current breaks ...
Text Solution
|
- A mutual inductor consists of two coils X and Y as shown in Fig. in wh...
Text Solution
|
- A long solenoid of length L, cross section A having N(1) turns has abo...
Text Solution
|
- A small coil of radius r is placed at the centre of a large coil of ra...
Text Solution
|
- The coefficient of mutual inductance of two circuits A and B is 3 mH a...
Text Solution
|
- Magnetic flux in a circular coil of resistance 10 Omega changes with t...
Text Solution
|