A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
HYDROCARBONS
NARAYNA|Exercise EXERCISE - 3|25 VideosHYDROCARBONS
NARAYNA|Exercise EXERCISE - 4|18 VideosHYDROCARBONS
NARAYNA|Exercise EXERCISE - 2 (H.W) (PROPERTIES OF ALKENES)|74 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
NARAYNA|Exercise Matrix-Match type questions|7 VideosHYDROGEN & ITS COMPOUCDS
NARAYNA|Exercise Interger type questions|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-HYDROCARBONS -EXERCISE - 2 (H.W) (PREPARATION & PROPERTIES)
- Three moles of glyoxal are obtained by the ozonolysis, followed by hyd...
Text Solution
|
- The product B is
Text Solution
|
- Amongst the following, the compound that can be most readily sulphonat...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following set of compounds in the order of their decreasin...
Text Solution
|
- DeltaH=-x" k.cal/mole" DeltaH=-y" k.cal/mole" The correct relati...
Text Solution
|
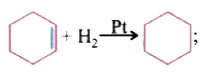 `DeltaH=-x" k.cal/mole"`
`DeltaH=-x" k.cal/mole"` 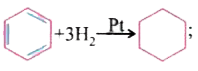 `DeltaH=-y" k.cal/mole"`
`DeltaH=-y" k.cal/mole"`