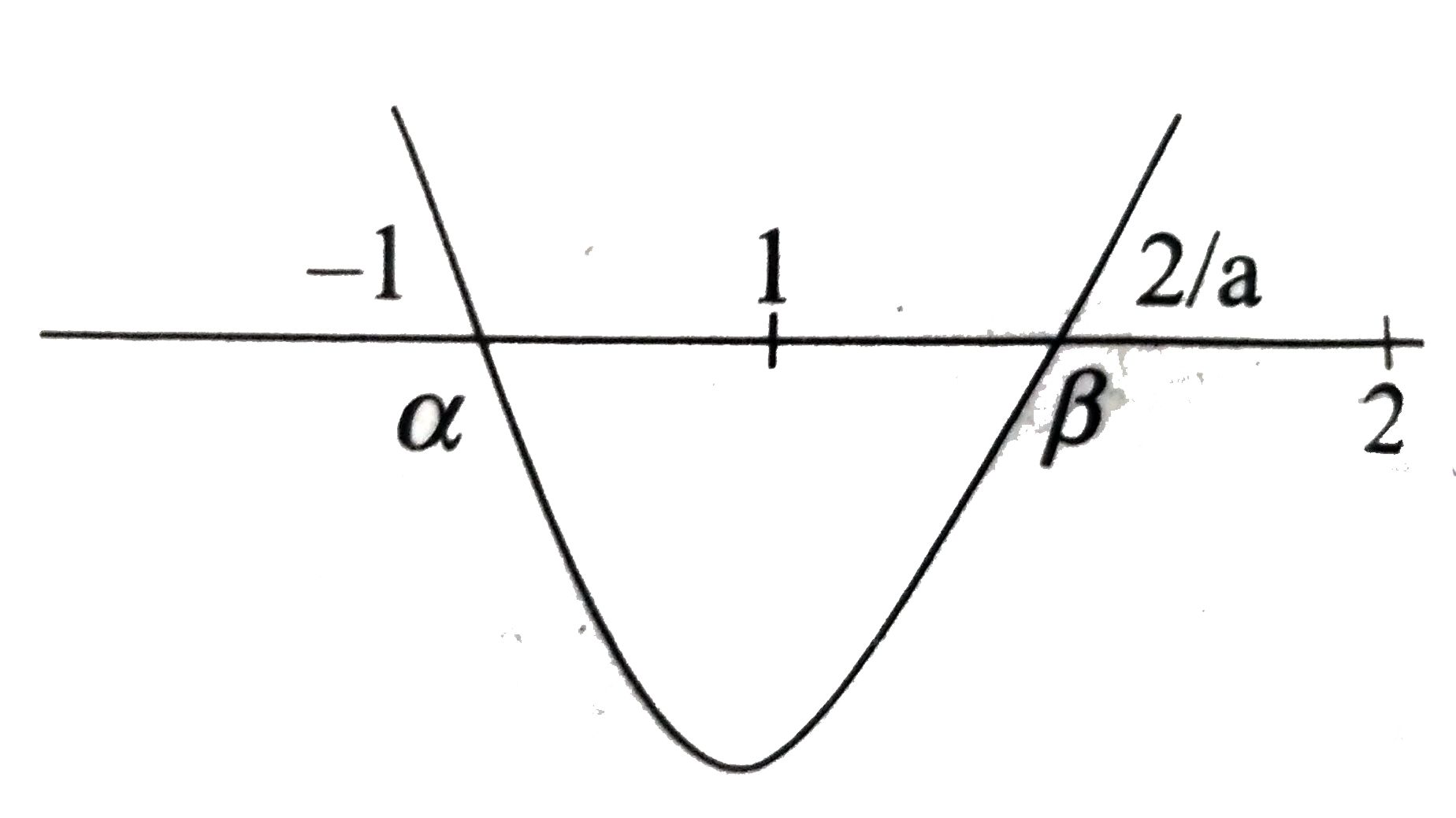
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE-THEORY OF EQUATIONS-JEE Advanced Previous Year
- The values of 'a' for which the quadraic expression ax^(2)+(a-2)x-2 is...
Text Solution
|
- Q. Let p and q real number such that p!= 0,p^2!=q and p^2!=-q. if alph...
Text Solution
|
- The value of b for which the equation x^2+bx-1=0 and x^2+x+b=0 have on...
Text Solution
|
- Let alpha and beta be the roots of x^2-6x-2=0 with alpha>beta if an=al...
Text Solution
|
- The quadratic equation p(x)=0 with real coefficients has purely imagin...
Text Solution
|
- Let -1/6 < theta < -pi/12 Suppose alpha1 and beta1, are the root...
Text Solution
|
- Let S be the set of all non-zero numbers alphasuch that the quadratic ...
Text Solution
|
- Let p ,q be integers and let alpha,beta be the roots of the equation, ...
Text Solution
|
- Let p ,q be integers and let alpha,beta be the roots of the equation, ...
Text Solution
|
- The number of distinct real roots of x^4-4x^3+12 x 62+x-1=0i sdot
Text Solution
|