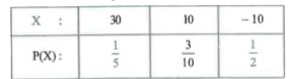
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
PROBABILITY
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise Objective Type Question (B. Fill in the Blanks)|15 VideosPROBABILITY
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise Objective Type Question (C. True/False Questions)|5 VideosPROBABILITY
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise EXERCISE 13 (h) (LATQ)|20 VideosMATRICES
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER TEST (3)|12 VideosRELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER TEST (1)|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-PROBABILITY-Objective Type Question (A. Multiple Choice Questions)
- Let A and B be two events such that P(A)=0.6, P(B)=0.2 and P(A//B)=0.5...
Text Solution
|
- If E and F are independent events such that 0ltP(E)lt1 and 0ltP(F)lt1,...
Text Solution
|
- Let 'X' be a discrete random variable. The probability distribution of...
Text Solution
|
- If X be a random variable taking values x(1),x(2),x(3),….,x(n) with pr...
Text Solution
|
- If A and B two events such that P(A)=0.2, P(B)=0.4 and P(A cup B)=0.5,...
Text Solution
|
- An urn contains 6 balls of which two are red and four are black. Two b...
Text Solution
|
- If E and F are independent events, P(E)=(1)/(2) and P(F)=(1)/(3), then...
Text Solution
|
- The probability of obtaining an even prime number on each die, when a...
Text Solution
|
- If P(A)=0.8, P(B)=0.5 and P(B/A)=0.4, then find P(A/B)
Text Solution
|
- If P(A)7/(13),P(B)=9/(13) and P(AnnB)=4/(13), find P(A/B)dot
Text Solution
|
- if A and B be two events such that P(A)=1/4, P(B)=1/3 and P(AuuB)=1...
Text Solution
|
- If P(A)=(1)/(2),P(B)=0, then P(A/B) is :
Text Solution
|
- The probability of obtaining an even prime number on each die, when a...
Text Solution
|
- If P (E) denotes probability of occurrence of event E, then :
Text Solution
|
- If A and B are independent events, then :
Text Solution
|
- The probability of obtaining an even prime number on each die, when a...
Text Solution
|
- If Aa n dB are two events such that P(A)=0. 5 ,P(B)=0. 6a n dP(AuuB)=0...
Text Solution
|
- If A and B are two independent events such that P(AuuB)=0. 60\ a n d\ ...
Text Solution
|
- Two cards are drawn from a well shuffled deck of $2 cards with replace...
Text Solution
|
- Events A and B are independent if
Text Solution
|