Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise NCERT FILE (NCERT EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS (OBJECTIVES QUESTIONS) (MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (TYPE-I))|13 VideosSYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise NCERT FILE (NCERT EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS (SUBJECTIVES QUESTIONS) (Very Short Answer Type Questions))|9 VideosSYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise NCERT FILE ( NCERT TEXTBOOK EXERCISES )|21 VideosPHYSICAL WORLD
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise Revision exercises (Long answer questions)|6 VideosTHERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE TEST|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION-NCERT FILE ( NCERT (ADDITIONAL EXERCISES) )
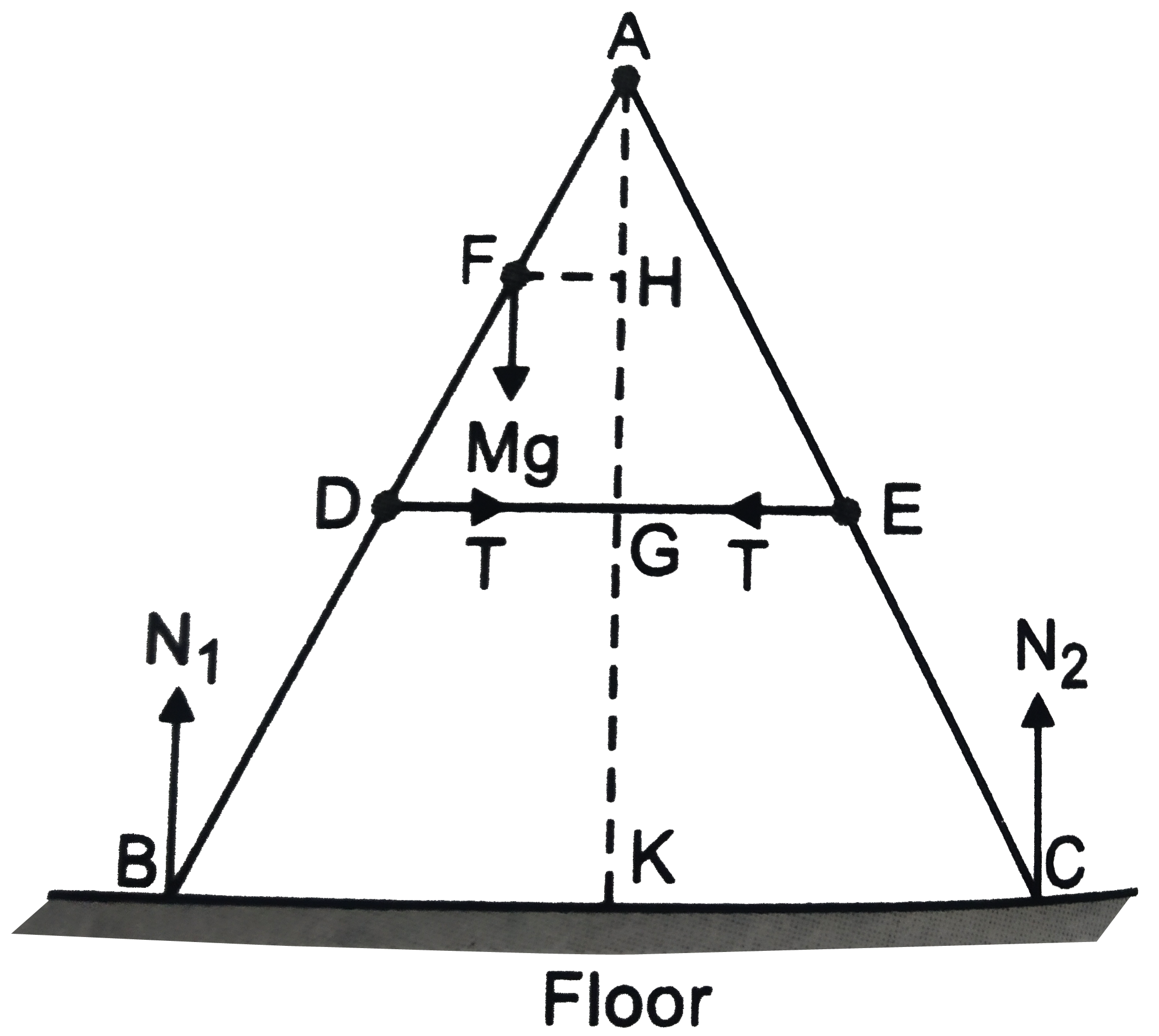
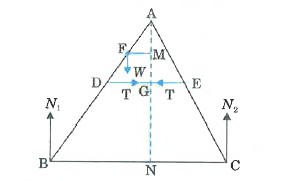
- As shown in Fig. the two sides of a step ladder BA and CA are 1.6 m lo...
Text Solution
|
- A man stands on a rotating platform, with his arms stretched horizonta...
Text Solution
|
- A bullet of mass 10 g and speed 500 m//s is fired into a door and gets...
Text Solution
|
- Two discs of moments of inertia I(1) and I(2) about their respective a...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Prove the theorem of perpendicular axes. (Hint : Square of the d...
Text Solution
|
- Prove the result that the velocity v of translation of a rolling body ...
Text Solution
|
- A disc rotating about its axis with angular speed omega(0) is placed l...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Explain why friction is necessary to make the disc to roll in the ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid disc and a ring, both of radius 10 cm are placed on a horizont...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder of mass 10 kg and radius 15 cm is rolling perfectly on a pl...
Text Solution
|
- Read each statement below carefully and state with reasons, if it is t...
Text Solution
|
- Separation of motion of a system of particles into motion of the centr...
Text Solution
|