A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise Competition File (C. MCQ With More Than One Correct Answers)|12 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise Competition File (D. MCQ Based On A Given Passage/Comprehension)|16 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise Competition File (JEE (Main) & Other State Boards For Engineering Entrance)|23 VideosMATHEMATICAL TOOLS
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise PRACTICE PROBLEMS (10)|12 VideosMOTION IN A PLANE
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise Chapter Practice Test|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS-Competition File (JEE (Advanced) For IIT Entrance)
- When liquid medicine of density rho is to put in the eye, it is done w...
Text Solution
|
- When liquid medicine of density rho is to be put in the eye, it is don...
Text Solution
|
- When liquid medicine of density rho is to be put in the eye, it is don...
Text Solution
|
- Water is filled in a container upto height 3m. A small hole of area 'a...
Text Solution
|
- Water is filled up to a height h in a beaker of radiys R as shown in t...
Text Solution
|
- Two soap bubbles A and B are kept in a closed chamber where the air is...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical vessel of height 500mm has an orifice (small hole) at it...
Text Solution
|
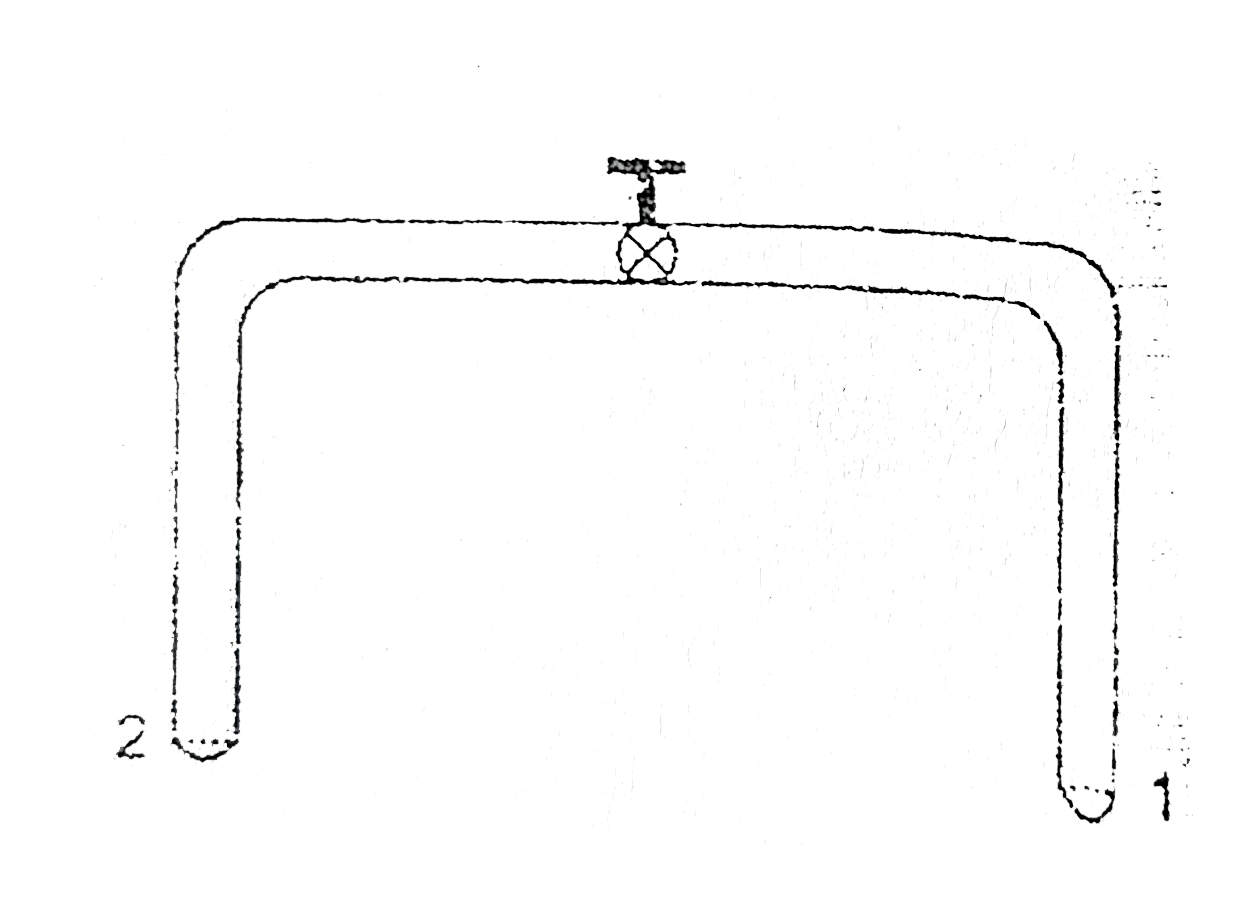
- A glass tube of uniform internal radius (r) has a valve separating the...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical solid ball of volume V is made of a material of density rh...
Text Solution
|
- A jar filled with two non-mixing liquid 1 and 2 having densities rho(1...
Text Solution
|
- A capillary tube (A) is dipped in water. Another identical tube (B) is...
Text Solution
|
- The pressure of a medium is charged from 1.01 xx 10. Pa to 1.165 xx 10...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the spring-mass system, with the mass submerged in water, as ...
Text Solution
|
- A glass capillary tube is of the shape of a truncated cone with an ape...
Text Solution
|