`f(x)="Maximum "{x^(2),(1-x^(2)),2x(1-x)}`
We draw the graphs of
`y=x^(2)" (1)"`
`y=(1-x^(2))" (2)"`
`y=2x(1-x)" (3)"`
Solving (1) and (3), we get `x^(2)=2x(1-x)`
`"or "3x^(2)=2xrArrx=0 or x=2//3.`
Solving (2) and (3) we get `(1-x)^(2)=2x(1-x)`
`rArr" "x=1//3 and x=1,`
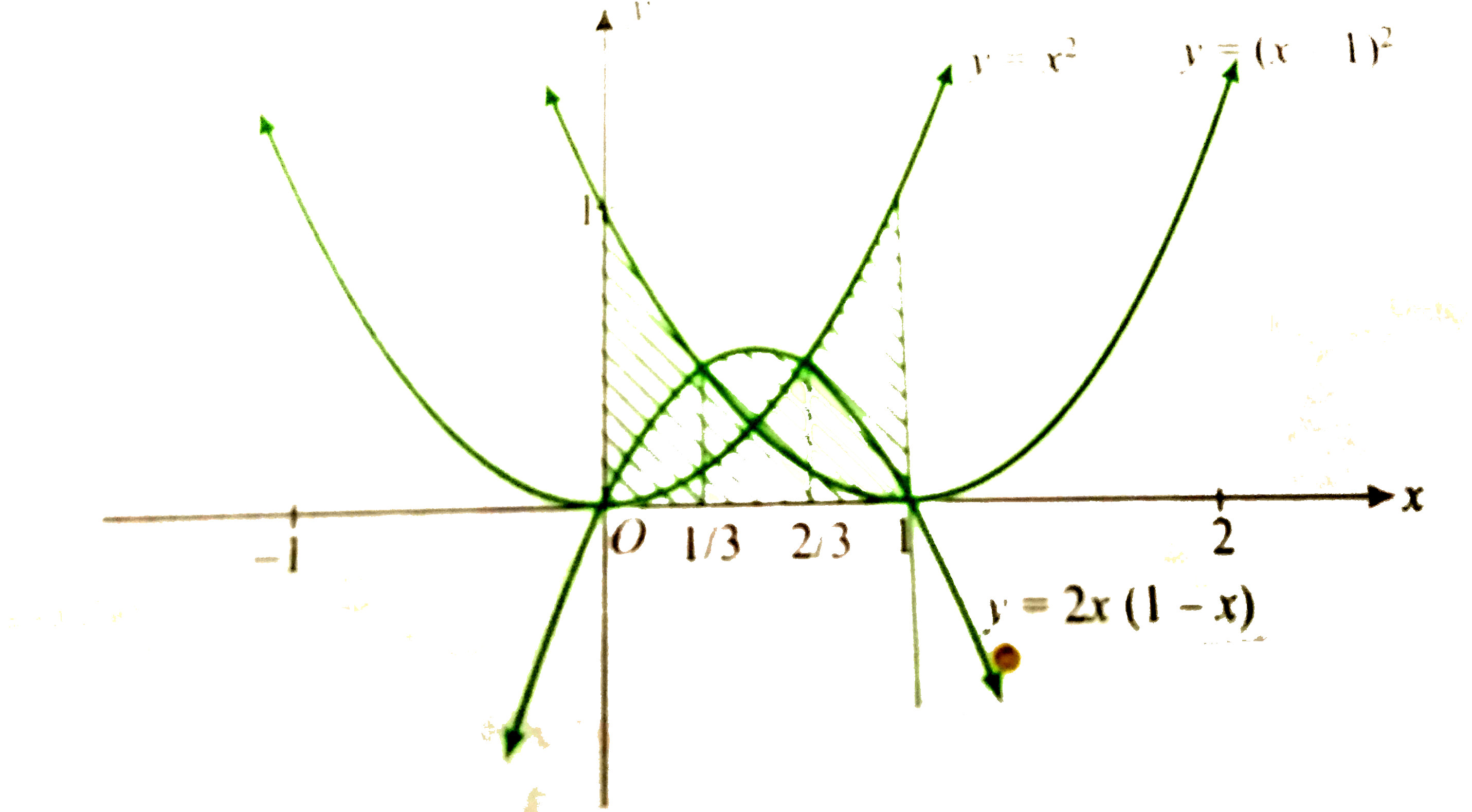
From the figure, it is clear that
`f(x){{:((1-x^(2)), "for ", 0le x le 1//3),(2x(1-x),"for ", 1//3 le x le 2//3),(x^(2), "for ", 2//3 lt x le 1):}`
The required area A is given by
`A=int_(0)^(1)f(x)dx`
`=f_(0)^(1//3)(1-x)^(2)dx+f_(1//3)^(2//3)2x(1-x)dx+int_(2//3)^(1)x^(2)dx`
`=-[(1)/(3)(1-x)^(3)]_(0)^(1//3)+[(x^(2)-(2x^(3))/(3))]_(1//3)^(2//3)+[(x^(3))/(3)]_(2//3)^(1)`
`=-(1)/(3)((2)/(3))^(3)+(1)/(3)+((2)/(3))^(2)-(2)/(3)((2)/(3))^(3)-((1)/(3))^(2)+(2)/(3)((1)/(3))^(3)+(1)/(3)-(1)/(3)((2)/(3))^(3)`
`=(17)/(27)` sq. units.