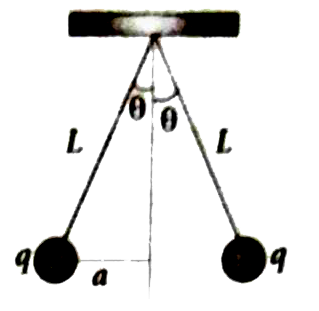
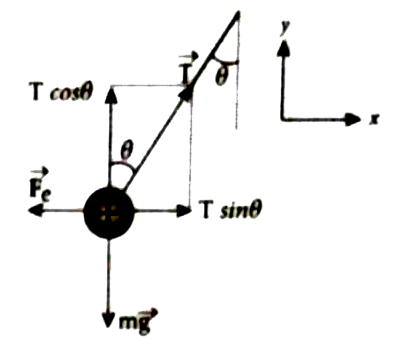
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROSTATICS
FULL MARKS|Exercise Textual Evaluation Solved (Multiple choice questions : )|15 VideosELECTROSTATICS
FULL MARKS|Exercise Textual Evaluation Solved (II. Short Answer Questions : )|21 VideosDUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
FULL MARKS|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS -( ADDITIONAL NUMERICAL PROBLEMS : )|10 VideosMAGNETISM AND MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
FULL MARKS|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS SOLVED - NUMERICAL PROBLEMS :|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FULL MARKS-ELECTROSTATICS -ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS SOLVED ( VII. NUMERICAL PROBLEMS )
- Two small -sized identical equally charged spheres each having mass 1 ...
Text Solution
|
- Electrons are caused to fall through a potential difference of 1500 vo...
Text Solution
|
- Small mercury drops of the same size are charged to the same potential...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles having charges Q(1) and Q(2) , when kept at a certain di...
Text Solution
|
- Two charges are placed in vacuum at a distance d apart. The force betw...
Text Solution
|
- Find the force of attraction between the plates of a parallel plate ca...
Text Solution
|