Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROSTATICS
FULL MARKS|Exercise EXERCISES|15 VideosELECTROSTATICS
FULL MARKS|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS SOLVED ( Multiple choice questions : )|57 VideosELECTROSTATICS
FULL MARKS|Exercise Textual Evaluation Solved (II. Short Answer Questions : )|21 VideosDUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
FULL MARKS|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS -( ADDITIONAL NUMERICAL PROBLEMS : )|10 VideosMAGNETISM AND MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
FULL MARKS|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS SOLVED - NUMERICAL PROBLEMS :|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FULL MARKS-ELECTROSTATICS -Textual Evaluation Solved ( III. Long Answer Questions: )
- Discuss the basic properties of electric charges.
Text Solution
|
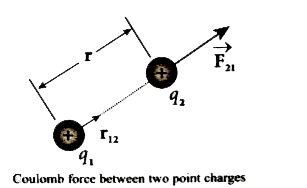
- Explain in detail Coulomb 's law and its various aspects.
Text Solution
|
- Define Electric field .
Text Solution
|
- How do we determine the electric field due to a continuous charge dist...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the electric field due to a dipole on its axial line and equ...
Text Solution
|
- Derive an expression for the torque experienced by a dipole due to a ...
Text Solution
|
- Derive an expression for electrostatic potential due to a point charge...
Text Solution
|
- Derive an expression for electrostatic potential due to an electric di...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain an expression for potential energy due to a collectrion of thre...
Text Solution
|
- Derive an expression for electrostatic potential energy of the dipole ...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain Gauss law from Coulomb 's law .
Text Solution
|
- Obtain the expression for electric field due to an infinitely long cha...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain the expression for electric field due to an charged infinite pl...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain the expression for electric field due to an uniformly charge sp...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the various properties of conductors in electrostatic equilibr...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the process of electrostatic induction .
Text Solution
|
- Explain dielectrics in detail and how an electric field is induced ins...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain the expression for capacitance for capacitance for a parallel p...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain the expression for the energy stored in a parallel plate capaci...
Text Solution
|
- Explain in detail the effect of a dielectric placed in a parallel plat...
Text Solution
|