Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
MOTION IN A PLANE
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise NCERT FILE (Solved) NCERT (Textbook Exercises)|25 VideosMOTION IN A PLANE
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise NCERT FILE (Solved) (NCERT (Additional Exercises))|7 VideosMOTION IN A PLANE
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise Conceptual Questions|23 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise Chapter Practise Test|16 VideosMOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE TEST|16 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-MOTION IN A PLANE -TOUGH & TRICKY PROBLEMS
- The resultant of two forces 3P and 2P is R. If the first force is doub...
Text Solution
|
- Three vectors are written as follows: vecA=-hati+2hatj+3hatk vecB...
Text Solution
|
- The force on a charged particle due to electric and magnetic fields is...
Text Solution
|
- It is given that |vecA(1)|=2,|vecA(2)|=3 and |vecA(1)+vecA(2)|=3 Fi...
Text Solution
|
- The sum of the magnitudes of two forces acting at a point is 16 N. The...
Text Solution
|
- Two towns A and B are connected by a regular bus service with a bus le...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected horizontal with a speed u from the top of pla...
Text Solution
|
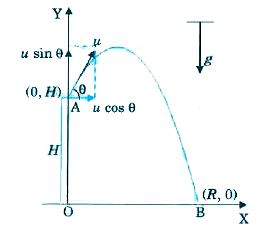
- A particle is projected from the top of a tower of height H. Initial v...
Text Solution
|
- In a criket match a batsman hits a six . Ball is hit 1 m above the gro...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles A and B are projected from the same point in different d...
Text Solution
|
- Points A and B are market on the ground at a distance 1 m from each ot...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected from origin at an angle is selected as X-axi...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is projected with initial speed u at an angle theta above the h...
Text Solution
|
- A man wishes to cross a river which is flowing at a certain speed . M...
Text Solution
|