Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
OPTICS
MBD -HARYANA BOARD|Exercise OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS|26 VideosOPTICS
MBD -HARYANA BOARD|Exercise SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS|46 VideosMODEL TEST PAPER - 2
MBD -HARYANA BOARD|Exercise SET - D ( LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS)|4 VideosPRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATION
MBD -HARYANA BOARD|Exercise Objective Type Questions|19 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MBD -HARYANA BOARD-OPTICS-LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
- The refractive index of a medium 'x' with respect to a medium 'y' is 2...
Text Solution
|
- Prove that (-mu1)/(u)+(mu2)/(v) = (mu2 - mu1)/( R) when refraction occ...
Text Solution
|
- An equiconvex lens of refractive index mu(2) is placed such that the r...
Text Solution
|
- An equiconvex lens of refractive index mu(2) is placed such that the r...
Text Solution
|
- Derive lens maker's formula for a thin biconvex lens.
Text Solution
|
- Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object pla...
Text Solution
|
- State and prove prism formula.
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the phenomenon of refraction through a prism. Prove that delta...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the ray diagram for simple microscope. Write expression for its ...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a labelled diagram of compound microscope. Derive expression for...
Text Solution
|
- The magnifying power of a compound microscope is
Text Solution
|
- Draw a labelled ray diagram showing the image formation in an astrono...
Text Solution
|
- Draw ray diagram for an astronomical telescope. Define magnification ...
Text Solution
|
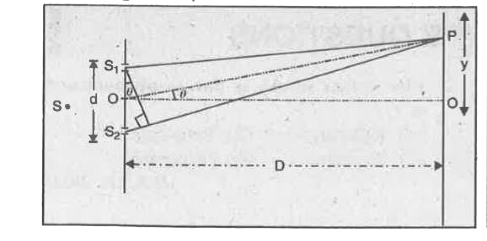
- Derive formula for fringe width using Young's double slit method for ...
Text Solution
|
- Define fringe width in interference and derive its expression.
Text Solution
|
- The fringe width in Young’s double slit experiment increases when
Text Solution
|
- Explain two methods of Polarisation.
Text Solution
|
- MALUS LAW
Text Solution
|