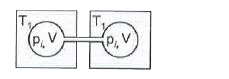
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
STATES OF MATTER : GASES AND LIQUIDS
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise COMPETITION FILE OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS (B. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS)(JEE (ADVANCED) FOR IIT ENTRANCE)|8 VideosSTATES OF MATTER : GASES AND LIQUIDS
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise COMPETITION FILE OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS (C. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS)|10 VideosSTATES OF MATTER : GASES AND LIQUIDS
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise COMPETITION FILE OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS (B. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS)|32 VideosSOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise COMPETITION FILE (INTEGER TYPE AND NUMERICAL VALUE TYPE QUESTIONS)|10 VideosSTRUCTURE OF ATOM
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise Unit Practice Test|13 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-STATES OF MATTER : GASES AND LIQUIDS-COMPETITION FILE OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS (B. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS)(JEE (MAIN) & OTHER STATE BOARDS FOR ENGINEERING ENTRANCE)
- The intermolecular interaction that is dependent on the inverse cube o...
Text Solution
|
- Dipole-dipole interaction energy between polar molecules in solids dep...
Text Solution
|
- A liquid can exist only
Text Solution
|
- Two closed bulbs of equal volume (V) containing an ideal gas initially...
Text Solution
|
- For same mass of two different ideal gases of molecular weights M(1) a...
Text Solution
|
- The dimension ML^(0)T^(-2) corresponds to .
Text Solution
|
- A gas will approach ideal behaviour at
Text Solution
|
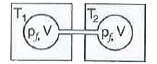
- What will be the relation between the T(1) of gas 1 with M(1)=56 and T...
Text Solution
|
- Which equation will explain the nature of PV versus P curve for CO(2) ...
Text Solution
|
- The value of compressibility factor (Z) for an ideal gas is
Text Solution
|
- Equal weights of ethane and hydrogen are mixed in an empty container a...
Text Solution
|
- An open vessel at 27^@C is heated untill two fifth of the air (assumed...
Text Solution
|
- The volume of gas A is twice than that of gas B. The compressibility f...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following equations does not represent Charles' law for a...
Text Solution
|
- Rare gases are sparingly soluble in water because of
Text Solution
|
- The volume of gas A is twice than that of gas B. The compressibility f...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the van der Waals constants, a and b, for the following gases...
Text Solution
|
- 0.5 moles of gas A and x moles of gas B exert a pressure of 200 Pa in ...
Text Solution
|
- An open vessel at 27^@C is heated untill two fifth of the air (assumed...
Text Solution
|
- Points I, II and III in the following plot respectively correspond to ...
Text Solution
|