A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GRAVITATION
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise COMPETITION FILE ( Jee (Advanced) for IIT Entrance)|6 VideosGRAVITATION
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise COMPETITION FILE ( C. Multiple Choice Questions)|12 VideosGRAVITATION
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise COMPETITION FILE (B.(Multipe Choice Questions from Competitive Examinations) AIPMT/NEET & Other State Boards for Medical Entrance)|16 VideosMATHEMATICAL TOOLS
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise PRACTICE PROBLEMS (10)|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-GRAVITATION-COMPETITION FILE (JEE (Main) & Other State Boards for Engineering Entrance )
- Take the mean distance of the moon and the sun from the earth to be0.4...
Text Solution
|
- The relative uncertainty in the period of a satellite orbiting around ...
Text Solution
|
- The height at which the acceleration due to gravity becomes (g)/(9) (w...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose that angular velocity of rotation of earth is increased. Then...
Text Solution
|
- If the angular momentum of a planet of mass m, moving around the Sun i...
Text Solution
|
- The energy required to take a satellite to a height ‘h’ above Earth su...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass m is moving in a circular orbit of radius R about a pla...
Text Solution
|
- Four particles, each of mass M and equidistant from each other, move a...
Text Solution
|
- From a solid sphere of mass M and radius R, a spherical portion of rad...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite is revolving in a circular orbit at a height 'h' from the ...
Text Solution
|
- The value of acceleration due to gravity at earth's surface is 9.8 ms^...
Text Solution
|
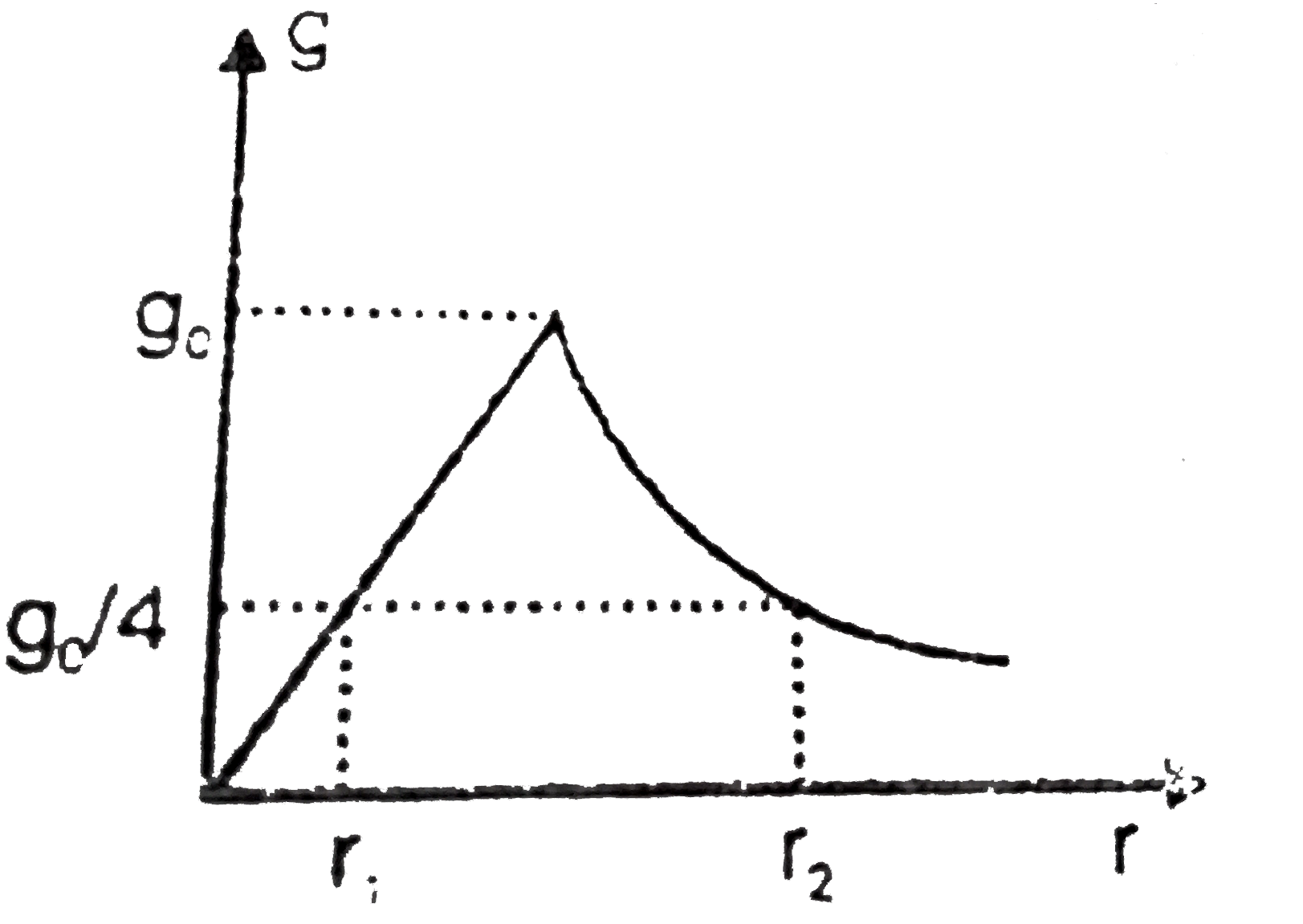
- Figure shows variation of acceleration due to gravity with distance fr...
Text Solution
|
- If the earth has no rotational motion, the weight of a person on the e...
Text Solution
|
- The mass density of a spherical body is given by rho(r)=k/r for r le R...
Text Solution
|
- A test particle is moving in a circular orbit in the gravitational fie...
Text Solution
|