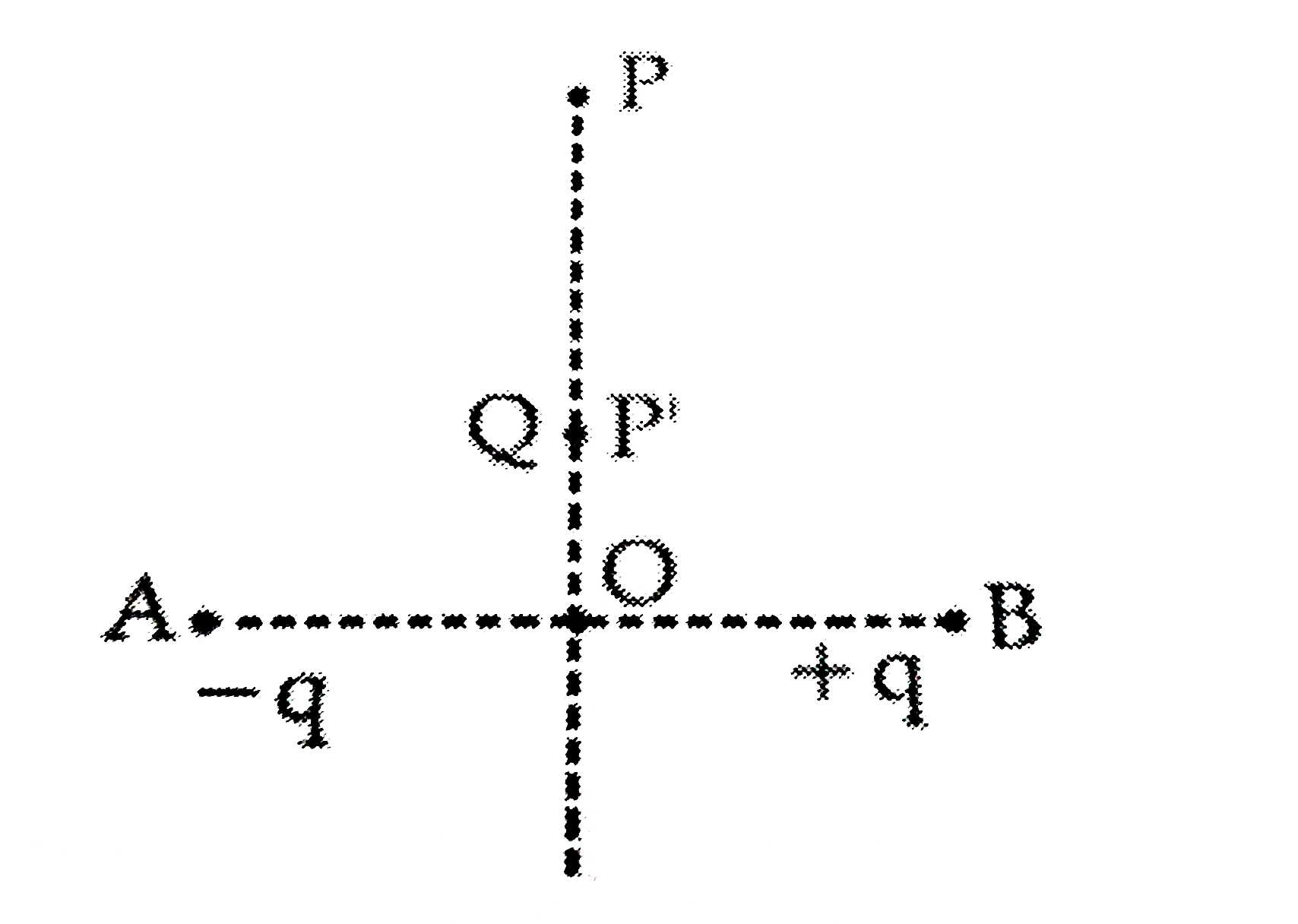Charges `-q and +q` located at A and B, respectively, constitute an electric dipole. Distance AB = 2a, O is the mid point of the dipole and OP is perpendicular to AB. A charge Q is placed at P where OP = y and `y gt gt 2a`. The charge Q experiences an electrostatic force F. If Q is now moved along the equatorial line to P' such that `OP' = ((y)/(3))`, the force on Q will be close to `((y)/(3) gt gt 2a)`