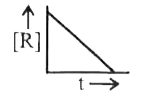
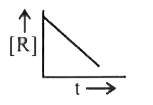
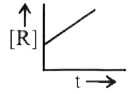
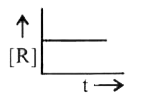
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL KINETICS
DISHA PUBLICATION|Exercise EXERCISE 1 : CONCEPT BUILDER (TOPICWISE)(TOPIC 3 : Theories of Rate of Reaction)|17 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
DISHA PUBLICATION|Exercise EXERCISE 2 : CONCEPT APPLICATOR|30 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
DISHA PUBLICATION|Exercise EXERCISE 1 : CONCEPT BUILDER (TOPICWISE) (TOPIC 1: Rate of Reaction, Rate Laws and Rate Constant)|11 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
DISHA PUBLICATION|Exercise EXERCISE-2: CONCEPT APPLICATOR|30 VideosCHEMISTRY IN EVERDAY LIFE
DISHA PUBLICATION|Exercise Exercise|88 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DISHA PUBLICATION-CHEMICAL KINETICS -EXERCISE 1 : CONCEPT BUILDER (TOPICWISE) (TOPIC 2: Order of Reaction and Half Life Period)
- A hypothetical reaction A(2) + B(2) rarr 2AB follows the mechanism as ...
Text Solution
|
- The time taken for 90% of a first order reaction to be completed is a...
Text Solution
|
- A substance 'A' decomposes by a first order reaction starting initial...
Text Solution
|
- Half life of a first order reaction is 4s and the initial concentrati...
Text Solution
|
- 3A to B+C, it would be a zero order reaction when
Text Solution
|
- The reaction A toB follows first order reaction. The time taken for 0....
Text Solution
|
- For a first-order reaction A rarr B the reaction rate at reactant conc...
Text Solution
|
- For a reaction A + 2B rarr C, rate is given by R = K [A] [B]^(2). The ...
Text Solution
|
- In a first order reaction, the concentration of the reactant, decrease...
Text Solution
|
- In a reaction, when the concentration of reactant is increased two ti...
Text Solution
|
- The rate constant of a first order reaction is 6.9xx10^(-3)s^(-1). How...
Text Solution
|
- The plot that represents the zero order reaction is:
Text Solution
|
- For a chemical reaction t(1 // 2) is 2.5 hours at room temperature. H...
Text Solution
|
- Point out the wrong statement: For a first order reaction
Text Solution
|
- For a reaction (d x)/(d t) = K[H^(+)]^(n). If pH of reaction medium ch...
Text Solution
|
- Ethylene is produced by C(4)H(8) overset(Delta)to 2C(2)H(4) The rat...
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following statements for the order of a reaction is i...
Text Solution
|
- The rate of a first-order reaction is 0.04 mol L^(-1)s^(-1) at 10 sec...
Text Solution
|
- Mechanism of a hypothetical reaction X(2) + Y(2) rarr 2XY is given b...
Text Solution
|
- A first order reaction has a specific reaction rate of 10^(-2) sec^(-1...
Text Solution
|