A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL KINETICS
DISHA PUBLICATION|Exercise EXERCISE 1 : CONCEPT BUILDER (TOPICWISE)(TOPIC 3 : Theories of Rate of Reaction)|17 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
DISHA PUBLICATION|Exercise EXERCISE-2: CONCEPT APPLICATOR|30 VideosCHEMISTRY IN EVERDAY LIFE
DISHA PUBLICATION|Exercise Exercise|88 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DISHA PUBLICATION-CHEMICAL KINETICS -EXERCISE 2 : CONCEPT APPLICATOR
- When ethyl acetate was was hydrolysedin presemce of 0.1 M HCl, the rat...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature dependence of rate constant (k) of a chemical reaction...
Text Solution
|
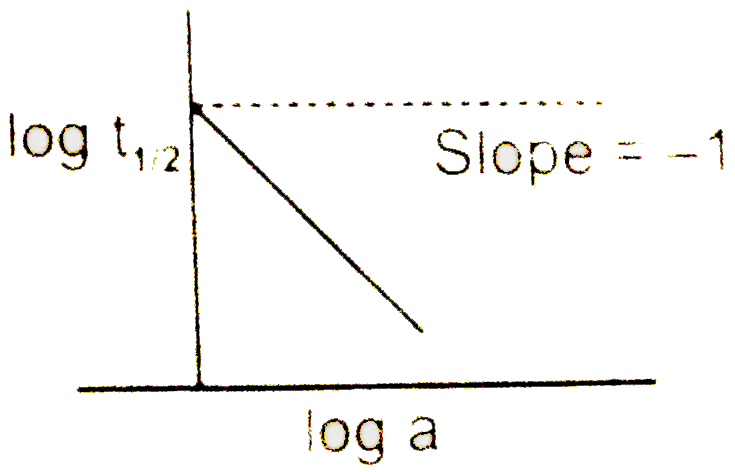
- A graph between log t((1)/(2)) and log a (abscissa), a being the init...
Text Solution
|
- The accompanying figure depicts a change in concentration of species A...
Text Solution
|
- Decomposition of NH(4)NO(2)(aq into N(2)(g) and 2H(2)O(l) is first ord...
Text Solution
|
- For a reaction Aoverset(k(r)=0.6M min^(-1))to2B starting with 1 M of...
Text Solution
|
- For an elementary reaction , X(g)toY(g)+Z(g) the half life period is...
Text Solution
|
- Consider following two competing first ordr reactions, Poverset(k(1)...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction (i) A overset(k(1))to P (ii) B overset(k(II))to...
Text Solution
|
- The decomposition of N(2)O(5) in carbon tetrachloride was followed by...
Text Solution
|
- The half-life of first order decomposition of NH(4)NO(3) is 2.10 hr at...
Text Solution
|
- The hydrolysis of sucrose was studied with the help of calorimeter and...
Text Solution
|
- The value of t(0.875)/(t(0.50) for n^(th) order reaction is
Text Solution
|
- In an attempt to compare the half-lives of two radioactive elements A...
Text Solution
|
- The initial rates ofreaction 3A + 2B + C to Products, at different ...
Text Solution
|
- The intergrated rate equation is Rt = log, C(0) - log C(t). The stra...
Text Solution
|
- The rate constant for a second order reaction is k=(2.303)/(t(a-b))log...
Text Solution
|
- The decomposition of N(2)O(5) occurs as, 2N(2)O(5) rarr4NO(2)+O(2) and...
Text Solution
|
- Graph between log k and 1//T [k rate constant (s^(-1)) and T and the t...
Text Solution
|
- For reaction A rarr B , the rate constant K(1)=A(1)(e^(-E(a(1))//RT)) ...
Text Solution
|