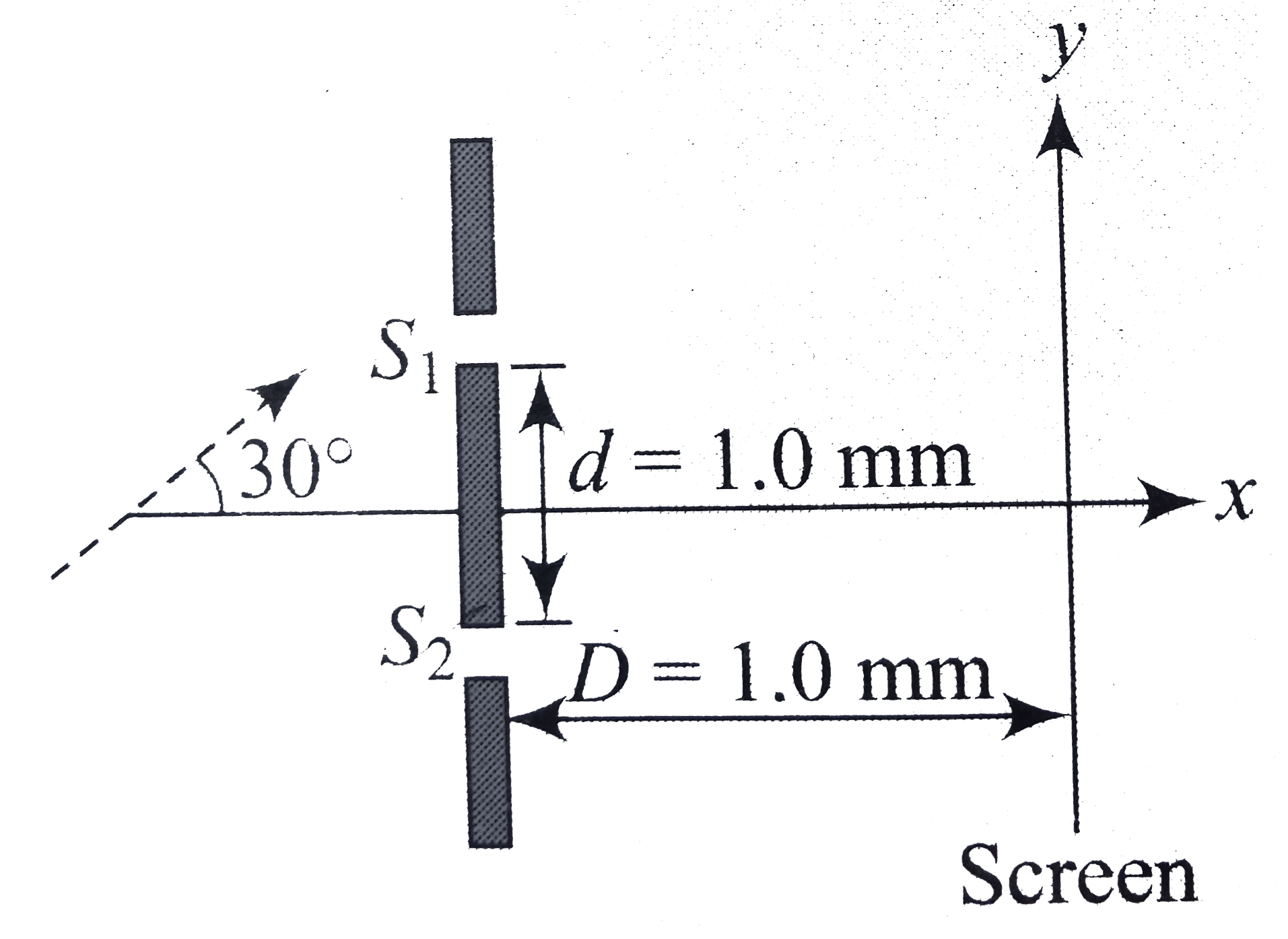When the incident beam falls nor- mally on the slits `S_(1)` and `S_(2)`, the path difference at the central point `P_(0)` of the screen is zero. Hence, we have the central maximum at `P_(0)`. At the minima, the path difference between the waves is `Delta=[m + (1 // 2)] lambda`.

This is a classic case when the wavelength of the light is comparable to the slit separation d. So we cannot apply the equation for fringe width as in Eq. 35-19.
Calculation: Let the minima appear along directions `theta` with respect to the incident direction. Coherent waves from `S_(1)` and `S_(2)` along this direction are brought to a focus at P. It is clear that the path difference between the waves from `S_(1)` and `S_(2)` on reaching P is
`Delta= d sin theta`.
The interference minima will appear on the screen if
`Delta=(m+(1)/(2))lambda`
`dsin theta=(m+(1)/(2))lambda`
where m is an integer. Thus, the direction of minima is given by
`sin theta =(m+(1)/(2)) xx (lambda)/(d)`
It is given that d = 1.0 mm and `lambda = 0.5 mm`. Therefore,
`sin theta =(m+(1)/(2)) xx ((0.5)/(1.0))=(1)/(2)(m+(1)/(2))" "(35-22)`
The allowed values of m are those integers for which `sin theta` is not more than +1 or less than -1. These values are m=1, 0, -1, and -2. Hence, four minima will be observed. If follows from the figure that
`tan theta=(y)/(D) implies y = D tan theta`
`y=(Dsin theta)/((1-sin^(2) theta)^(1 // 2))" "(35-23)`
The first minima above the central maximum (`P_(0)`) corresponds to m = 0. Using Eq. 36-17, we have `sin theta=1 // 4` for this minimum. Using this value in Eq. 35-22 the distance of the first minimum `P_(1)` from `P_(9)` is
`y_(1)=((1.0 m) xx (1 // 4))/([1-(1 //16)]^(1 // 2))=(1)/(sqrt(15)) m`.
This is the y coordinate of the first minimum `P_(1)` above `P_(0)`.
The second minima above `P_(0)` corresponds to m = 1, for which, we have from Eq. 36-17, `sin theta = 3 // 4`. Using this value in Eq. 35-24, the y coordinate of the second minimum `P_(2)` above `P_(1)` is
`y_(2)=((1.0 m) xx (3 // 4))/([1-(9 // 16)]^(1 // 2))=(3)/(sqrt7)m`
The first minimum `P_(1).`below `P_(0)` corresponds to m = -1, for which `sin theta = -1 // 4`. The y coordinate of this minimum `P_(1).` is
`y_(1).= -(1)/(sqrt(15)) m`.
The second minimum below `P_(2).` corresponds to m= -2 for which `sin theta = -3 // 4`. The y coordinate of `P_(2).` is
`P_(2).= -(3)/(sqrt7) m.` (Answer)