Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT BANGLISH-TRIANGLES -EXERCISE - 7.1
- In quadrilateral ACBD, AC = AD and AB bisects /A Show that DeltaABC~= ...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AD = BC and/ DAB = / CBA Prove that ...
Text Solution
|
- AD and BC are equal and perpendiculars to a line segment AB. Show that...
Text Solution
|
- l and m are two parallel lines intersected by another pair of parallel...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjacent figure, AC = AE, AB = AD and / BAD = / EAC. Show that ...
Text Solution
|
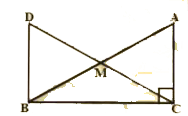
- In right triangle ABC, right angle is at C, M is the mid-point of hypo...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjacent figure ABCD is a square and Delta APB is an equilatera...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjacent figure DeltaABC is isosceles as bar(AB) = bar(AC), bar...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjacent figure DeltaABC, D is the midpoint of BC. DE|AB, DF|AC...
Text Solution
|
- If the bisector of an angle of a triangle also bisects the opposite si...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure ABC is a right triangle and right angled at B such...
Text Solution
|