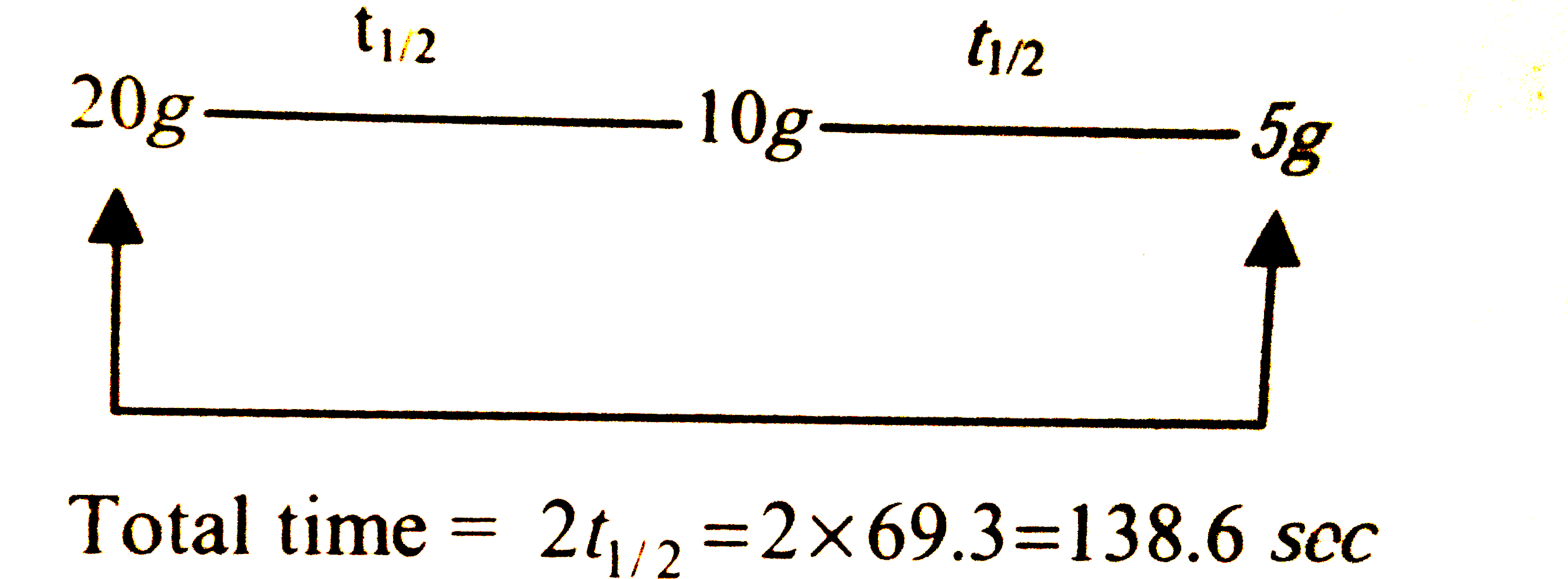A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL KINETICS
ERRORLESS |Exercise Ordinary Thinking (Collision theory , Energy of activation and Arrhenius equation )|45 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
ERRORLESS |Exercise Critical Thinking Objective Questions|20 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
ERRORLESS |Exercise JEE (Advanced ) 2018|1 VideosCHEMICAL EQULIBRIUM
ERRORLESS |Exercise JS JEE SECTION (ONLY ONE CHOICE ANSWER (Matrix)|1 VideosCHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY IN LIFE
ERRORLESS |Exercise Critical Thinking (Objective question )|25 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ERRORLESS -CHEMICAL KINETICS -Ordinary Thinking (Rate law and Rate constant )
- The reaction 2H2O2 to 2H2O + O2 is a
Text Solution
|
- Rate constant for a reaction H(2) + I(2) rarr 2HI is 49, then rate con...
Text Solution
|
- For a first order reaction , rate constant is 0.6932 "hr"^(-1) , then...
Text Solution
|
- Unit of K for third order reaction is
Text Solution
|
- A reaction is of the first order reaction to A and is of second order ...
Text Solution
|
- The half-life period for a first order reaction is:
Text Solution
|
- The value of rate constant for a first order reaction is 2.30...
Text Solution
|
- For a reaction A rarr B, the rate of reaction quadrupled when the conc...
Text Solution
|
- The rates of a certain reaction (dc/dt) at different times are as foll...
Text Solution
|
- By the overall order of a reaction , we mean
Text Solution
|
- In presence of HCl, sucrose gets hydrolysed into glucose and fructose....
Text Solution
|
- Integrated velocity equation for first order reaction is
Text Solution
|
- Assertion. Average life of a radioactive element is that period in whi...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : The hydrolysis of methyl acetate by dil. HCl is a pseudo f...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) : The order of a reaction can have fractional value Re...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Molecularity greater than three is not observed. Reason ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: Half-life period of a reaction of first order is independen...
Text Solution
|
- A first order reaction has a specific reaction rate of 10^(-2) sec^(-1...
Text Solution
|
- The correct difference between first and second order reactions is tha...
Text Solution
|
- When initial concentration of the reactant is doubled, the half-life p...
Text Solution
|