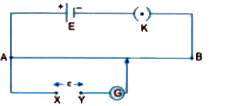
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CURRENT ELECTRICITY
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS - II|8 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SELF ASSESSMENT TEST (SECTION A (MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS))|6 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS|42 VideosCBSE SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER 2019-20 (SOLVED)
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SECTION D|6 VideosDUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SELF ASSESSMENT TEST SECTION-C (VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS)|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
U-LIKE SERIES-CURRENT ELECTRICITY -LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS - I
- In a metre bridge the null point is found at a distance of 60.0 cm fro...
Text Solution
|
- The reading of an ideal ammeter, in the circuit shown here, equals (i)...
Text Solution
|
- For the potentiometer circuit shown in the given figure, points X and ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) For the circuit shown in the figure, how would the balancing lengt...
Text Solution
|
- Two cells of emf 1.5 V and 2 V and internal resistance 1Omega and 2Ome...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the value of the resistance R in the circuit shown in Fig. s...
Text Solution
|
- Using Kirchhoff's rules determine the value of unknown resistance R in...
Text Solution
|
- State Kirchhoff's rules of current distribution in an electrical netwo...
Text Solution
|
- State Kirchhoff's rules. Use these rules to write the expressions for ...
Text Solution
|
- State Kirchhoff's rules. Apply these rules to the loops PRSP and PRQP...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown , R1=4Omega, R2=R3 =15Omega, R4 = 30 Omega and e...
Text Solution
|
- Two cells of same emf epsi but internal resistances r1 and r2 are co...
Text Solution
|
- In the electric network shown in the Fig., use Kirchhoff's rules to ca...
Text Solution
|
- Using Kirchhoff's rules, calculate the potential difference between B ...
Text Solution
|
- Two heating elements of resistances R1 and R2 when operated at a cons...
Text Solution
|
- A potentiometer wire of length 1 m is connected to a driver cell of e...
Text Solution
|
- A 10 m long wire of uniform cross-section and 20Omega resistance is u...
Text Solution
|
- A circuit using a potentiometer and battery of negligible internal res...
Text Solution
|
- In the Fig., a long uniform potentiometer wire AB is having a constan...
Text Solution
|
- Two conductors are made of the same material and have the same length....
Text Solution
|