Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RS AGGARWAL-COORDINATE GEOMETRY-Exercise 6D
- Points A(-1, y) and B(5, 7) lie on a circle with centre O(2, -3y) . Fi...
Text Solution
|
- If the point A(0, 2) is equidistant from the points B(3, p) and C(p, 5...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is rectangle whose three vertices are B(4, 0), C(4, 3) and D(0, 3...
Text Solution
|
- If the point P(k-1, 2) is equidistant from the point A(3, k) and B(k,...
Text Solution
|
- Find the ratio in which the point P(x, 2) divides the join of A(12, 5)...
Text Solution
|
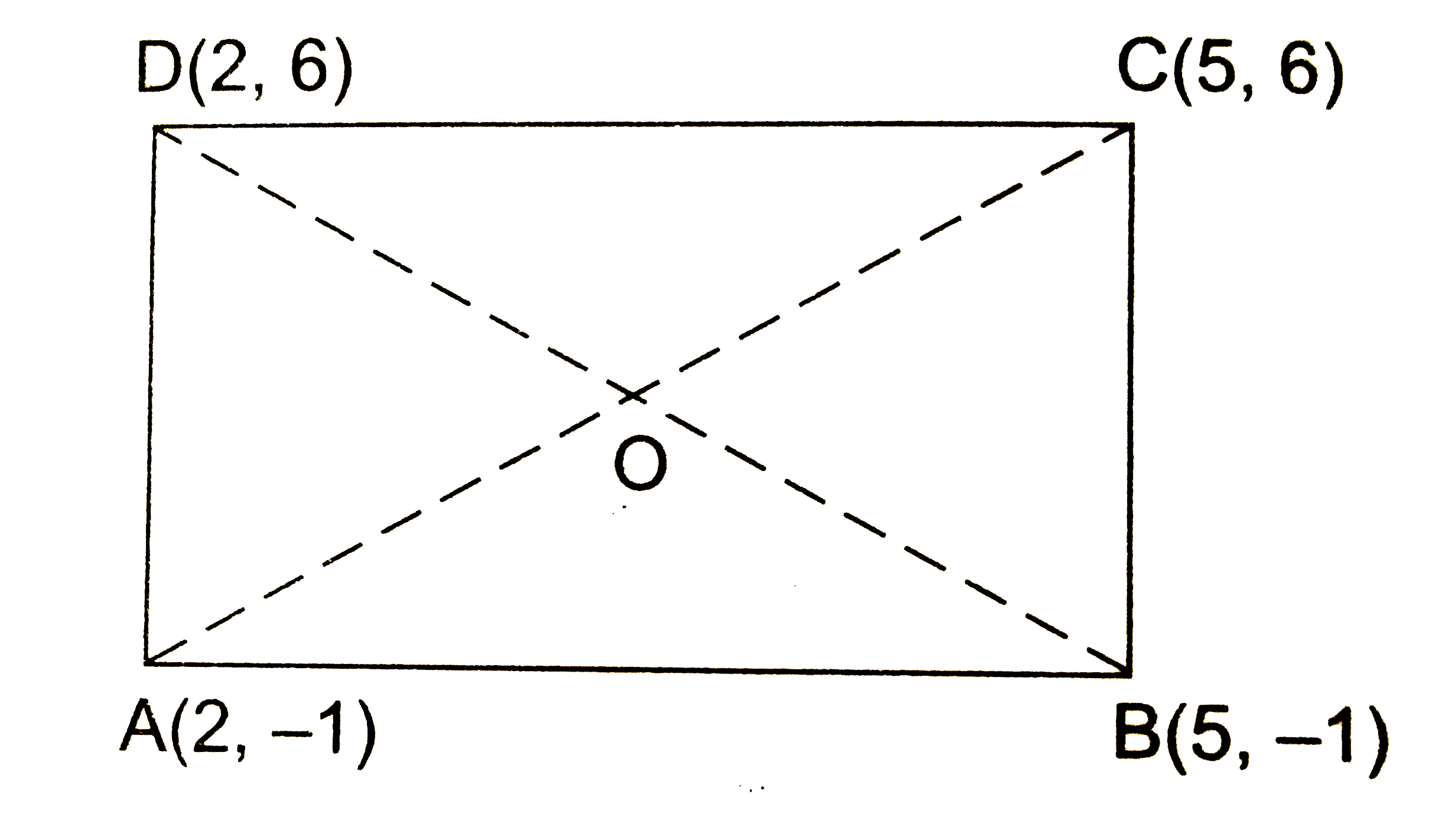
- Prove that the diagonals of a rectangle ABCD with vertices A(2, -1), B...
Text Solution
|
- Find the lengths of the medians AD and BE of Delta ABC whose vertices ...
Text Solution
|
- If the point C(k, 4) divides the join of A(2, 6) and B(5, 1) in the ra...
Text Solution
|
- Find the point on x-axis which is equidistant from points A(-1, 0) and...
Text Solution
|
- Find the distance between the points ((-8)/(5), 2) "and" ((2)/(5), 2)
Text Solution
|
- Find the value of a so that the point (3,a) lies on the line represent...
Text Solution
|
- If the points A(4, 3) and B(x, 5) lie on a circle with the centre O(2,...
Text Solution
|
- If P(x, y) is equidistant from the points A(7, 1) and B(3, 5), find th...
Text Solution
|
- If the centroid of Delta ABC having vertices A(a, b), B(b, c) and C(c,...
Text Solution
|
- Find the centroid of Delta ABC whose vertices are A(2, 2), B(-4, -4) a...
Text Solution
|
- In what ratio does the point C(4, 5) divide the join of A(2, 3) and B(...
Text Solution
|
- If the points A(2, 3), B(4, k) and C(6, -3) are collinear, find the va...
Text Solution
|