KEY IDEA
If `vecF_(1)` is the force on the proton due to charge `q_(1)` and `vecF_(1)` is the force on the proton due to charge `q_(2)`, then the point we seek is where Thus, `vecF_(1)+vecF_(2)=0`. Thus,
`vecF_(1)=-vecF_(2) " " (22-8)`
This tells us that at the point we seek, the forces acting on the proton due to the other two particles must be of equal magnitudes
`vecF_(1)=vecF_(2), " " (22-9)`
and that the forces must have opposite directions.
Reasoning : Because a proton has a positive charge, the proton and the particle of charge `q_(1)` are of the same sign, and force `vecF_(1)` on the proton must point away from `q_(1)`. Also, the proton and the particle of charge `q_(2)` are of opposite signs, so force `vecF_(2)` on the proton must point toward `q_(2)`. "Away from `q_(1)`" and "toward `q_(2)`" can be in opposite directions only if the proton is located on the x axis.
If the proton is on the x axis at any point between `q_(1)` and `q_(2)`, such as point P in Fig. 22-9b, then `vecF_(1) and vecF_(2)` are in the same direction and not in opposite directions as required. If the proton is at any point on the x axis to the left of `q_(1)`, such as point S in Fig. 22-9c, then `vecF_(1)` and `vecF_(2)` are in opposite directions. However, Eq. 22-4 tells us that `vecF_(1) and vecF_(2)` cannot have equal magnituded there: `F_(1)` must be greater than `F_(2),` because `F_(1)` is produced by a closer charge (with lesser r) of greater magnitude (8q versus 2q).
Finally, if the proton is at any point on the x axis to the right of `q_(2)`, such as point R in Fig. 22-9d, then `vecF_(1) and vecF_(2)` are again in opposite directions. However, because now
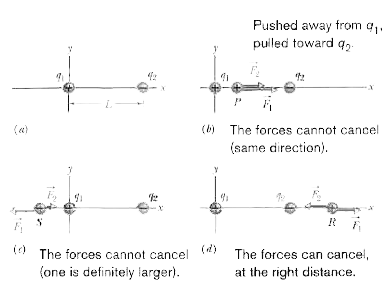
the charge of greater magnitude `(q_(1))` is farther away from the proton than the charge of lesser magnitude, there is a point at which `F_(1)` is equal to `F_(2)`. Let x be the coordinate of this point, and let `q_(p)` be the charge of the proton.
Calculations: With Eq. 22-4, we can now rewrite Eq. 22-9:
`(1)/(4pi epsilon_(0)) (8qq_(p))/(x^(2))=(1)/(4pi epsilon_(0)) (2q q_(0))/((x-L)^(2)). " " (22-10)`
Rearranging Eq. 22-10 gives us
`((x-L)/(x))^(2)=(1)/(4)`
After taking the square roots of both sides, we find
`(x-L)/(x)=(1)/(2)`
and x = 2L. (Answer)
The equilibrium at x = 2L is unstable, that is, if the proton is displaced leftward from point R, then `F_(1) and F_(2)` both increase but `F_(2)` increases more (because `q_(2)` is closer than `q_(1)`), and a net force will drive the proton farther leftward. If the proton is displaced reightward, both `F_(1) and F_(2)` decrease but `F_(2)` decrease more, and a net force will then drive the protonfarther rightward. In a stable equilibrium, if the proton is displaced slightly, it returns to the equilibrium position.
