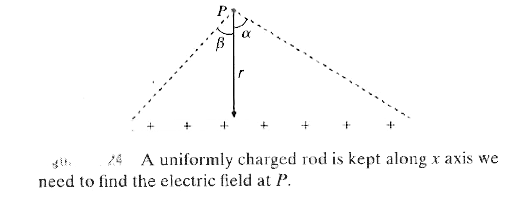KEY IDEA
Because the rod has a continuous charge distribution, we must find an expression for the electric fields due to differential elements of the rod and then sum those fields via calculus.
Calculations : An element : Consider a differential element having length dx. If the length of a line segment is dx, the charge on it is `lambda dx`. Here `lambda` is the charge per unit length of the line (assumed to be constant).
Thus,
`dq=lambda dx`.
The element.s field: Our element produces a differential electric field. Treating this element as a point charge, the electric field due to this small charge at a distance r from the line is
`dE=(k lambda dx)/((sqrt(x^(2)+r^(2))^(2)))`.
The electric field is away from the charge because the charge is positive .
Summing: Thus, to find the electric field set up by the rod, we need sum (via integration) the parallel as well as perpendicular components of the differential electric field is setup by all the differential elements of the rod.
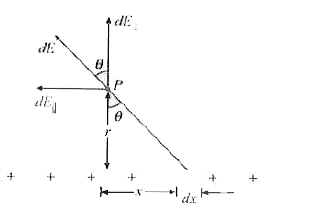
Let us resolve this electric field in a direction parallel and perpendicular to the line charge.
`dE_("||")=dEsin theta`,
`dE_(bot)=dE cos theta`,
`dE_("||")=(k lambda dx)/((x^(2)+r^(2))) sin theta`.
From the geometry of Fig. 22-25, we can say that
`(x)/(r )=tan theta`,
`x= r tan theta`.
Since we need to replace x everywhere by the variable `theta`, we need to differentiate this expression with respect to `theta`.
`(dx)/(d theta)=r sec^(2) theta`,
`dx=r sec^(2)theta d theta`.
By replacing this expression for dE, we get
`dE_("||")=(k lambda xx r sec^(2)theta xx sin theta)/((r^(2)+r^(2)tan^(2)theta)) d theta`,
`dE_("||")=(k lambda)/(r ) sin theta d theta`,
`E_("||")=(k lambda)/(r ) int_(-beta)^(alpha) sin theta d theta `
`=(k lambda)/(r )[cos alpha-cos(-beta)]=(k lambda)/(r )[cos beta-cos alpha]`.
Similarly resolving the electric field in the perpendicular direction, we have
`E_(bot)=(k lambda)/(r ) int_(-beta)^(a) cos theta d theta`
`=(k lambda)/(r )[ sin alpha+sin beta]`
Note: If the line is infinite which means that it extends from `-oo` to `+oo`, we can assume `alpha=90^(@) and beta=90^(@)`.
Then `E_("||")=(k lambda)/(r )[cos90^(@)-cos90^(@)]=0`
`E_(bot)=(k lambda)/(r )[sin 90^(@)-sin90^(@)]=(2k lambda)/(r )`.
If the line is semi-infinite, extending from `-oo` to the foot of the perpendicular, we can assume `alpha=90^(@) and beta=0^(@)`.
Then
`E_("||")=(k lambda)/(r )[cos0^(@)-cos90^(@)]=(k lambda)/(r )`
`E_(bot)=(k lambda)/(r )[sin 90^(@)-sin0^(@)]=(k lambda)/(r )`.