Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROCHEMISTRY
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise CASE BASED/SOURCE-BASED INTEGRATED QUESTIONS (LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS-I (3 MARKS EACH))|27 VideosELECTROCHEMISTRY
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise CASE BASED/SOURCE-BASED INTEGRATED QUESTIONS (LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS-II (5 MARKS EACH))|16 VideosELECTROCHEMISTRY
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise CASE BASED/SOURCE-BASED INTEGRATED QUESTIONS (VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS (1 MARK EACH))|47 VideosCOORDINATION COMPOUNDS
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SELF ASSESSMENT TEST|7 VideosEXAMINATION PAPER 2020
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SECTION D|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
U-LIKE SERIES-ELECTROCHEMISTRY -CASE BASED/SOURCE-BASED INTEGRATED QUESTIONS (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS (2 MARKS EACH))
- Describe the construction of a H(2)-O(2) , fuel cell and the reactions...
Text Solution
|
- The following curve is obtained when molar conductivity Lambda(m) is p...
Text Solution
|
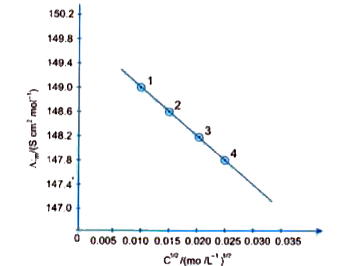
- The molar conductivity (Lambda(m)) of KCl solutions at different conce...
Text Solution
|
- (i) For a weak electrolyte molar conductance in dilute solution increa...
Text Solution
|
- Write the chemical equations for all the steps involved in the rusting...
Text Solution
|
- Value of standard electrode potential for the oxidation of Cl^(-) ions...
Text Solution
|
- Aqueous copper sulphate solution and aqueous silver nitrate solution a...
Text Solution
|
- How long a current of 3 amperes has to be passed through a solution of...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following diagram in which an electrochemical cell is cou...
Text Solution
|
- What advantages do the fuel cells have over primary and secondary batt...
Text Solution
|
- Write the Nernst equation for the cell reaction in the Daniel cell. Ho...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a cell given below: Cu | Cu^(2+) || Cl^(-) | Cl(2),Pt Wri...
Text Solution
|
- Write the cell reaction of a lead storage battery when it is discharge...
Text Solution
|
- Solutions of two electrolytes 'A' and 'B' are diluted. The Lambda(m) ...
Text Solution
|
- Blue colour of copper sulphate is slowly discharged when an iron rod i...
Text Solution
|
- Why on dilution the Lambda(m) of CH3COOH increases drastically, while...
Text Solution
|
- On the basis of the standard electrode potential values stated for aci...
Text Solution
|
- Estimate the minimum potential difference required to reduce Al(2)O(3)...
Text Solution
|
- The resistance of conductivity cell containing 0.001 M KCl solution at...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why electrolysis of aqueous solution of NaCl gives H(2) at ca...
Text Solution
|