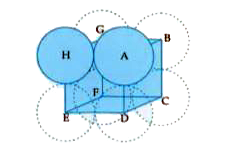
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SOLID STATE
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise LONG ANSWER QUESTION - I|20 VideosSOLID STATE
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SELF ASSESSMENT TEST|8 VideosSOLID STATE
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS|35 VideosSAMPLE QUESTIONS PAPER
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SECTION D|6 VideosSOLUTION
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SELF ASSESSMENT TEST (SECTION D)|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
U-LIKE SERIES-SOLID STATE-SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
- How do you explain the fluidity of liquids and gases and rigidity of s...
Text Solution
|
- Classify quartz and glass into the type of solids they are. What makes...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the packing efficiency of a metal crystal for a simple cubic...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following terms with suitable example of each : (i) Fer...
Text Solution
|
- In terms of band theory, explain the difference between a conductor an...
Text Solution
|
- Explain anisotropy in solids with the help of a diagram.
Text Solution
|
- Distinguish between crystalline and amorphous solids in terms of (a)...
Text Solution
|
- Sodium crystallises in a bcc unit cell. Calculate the approximate numb...
Text Solution
|
- What is a semiconductor ? Describe the two main types of semiconductor...
Text Solution
|
- The well-known mineral fluorite is chemically calcium fluoride. It is ...
Text Solution
|
- What is a unit cell ? What are its parameters ? Show them by drawing a...
Text Solution
|
- Give one example each of hydrogen bonded molecular solid and network s...
Text Solution
|
- KF has ccp structure . Calculate the radius of unit cell if the side o...
Text Solution
|
- Give reason : ( a ) Why is Frenkel defect found in AgCl ? ( b ) W...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following terms with suitable examples : ( a ) Schottky ...
Text Solution
|
- Why are liquids and gases categorised as fluids ?
Text Solution
|
- Why are solids incompressible ?
Text Solution
|
- Give the contribution of the following to the unit cell : (a) An ato...
Text Solution
|
- (a) How are tetrahedral and octahedral holes formed ? (b) If N is ...
Text Solution
|
- Inspite of long range order in the arrangement of particles why are th...
Text Solution
|