Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY-WORK, POWER, AND ENERGY-PRACTICE QUESTIONS (Integer Type)
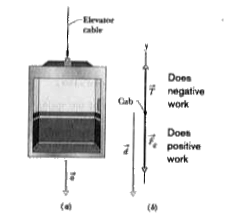
- An elevator cab of mass m=500 kg is descending with speed v(i)=4.0m//s...
Text Solution
|
- A 10 kg mass moves x-axis. Its acceleration as function of its positio...
Text Solution
|
- A car of mass 900 kg accelerates uniformly from rest to a speed of 60 ...
Text Solution
|
- If the speed of a car increases 4 times, the stopping distance ( in m)...
Text Solution
|
- A swimmer moves through the water at a speed of 0.22 m/s. The drag for...
Text Solution
|
- A river descends 15 m through rapids. The speed of the water is 3.2 m...
Text Solution
|