Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
THE HUMAN EYE AND THE COLOURFUL WORLD
ZEN PUBLICATION|Exercise ZEN ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS SECTION - HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS (HOTS)|26 VideosTHE HUMAN EYE AND THE COLOURFUL WORLD
ZEN PUBLICATION|Exercise ZEN ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS SECTION - SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS - II|28 VideosSOURCES OF ENERGY
ZEN PUBLICATION|Exercise ZEN ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS SECTION (HIGHER-ORDER THINKING SKILLS [HOTS] )|14 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ZEN PUBLICATION-THE HUMAN EYE AND THE COLOURFUL WORLD-ZEN ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS SECTION - Problem Section
- What is atmospheric refraction ? Use this phenomenon to explain the fo...
Text Solution
|
- What is Tyndall effect? What is its cause ? Name two phenomena observe...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of light is allowed to pass through two beakers A and B, contai...
Text Solution
|
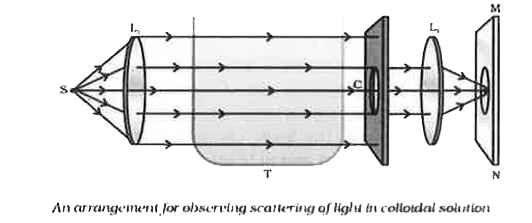
- Write an activity for observing scattering of light in colloidal solut...
Text Solution
|
- Mention any four differences between a glass slab and a glass prism.
Text Solution
|
- Calculate maximum power of accomodation of a person having normal visi...
Text Solution
|
- How can we determine the focal length and power of the concave lens re...
Text Solution
|
- How can we determine the focal length and power of the convex lens req...
Text Solution
|
- A person with a myopia eye cannot see objects beyond a distance of 1.5...
Text Solution
|
- A doctor prescribes a corrective lens of power -0.5 D to a person. Fin...
Text Solution
|
- Why does the power to clearly see near objects and far-off objects dim...
Text Solution
|
- The far point of a myopia eye is 60 cm. Find the focal length of the l...
Text Solution
|
- Ravi kept a book at a distance of 10 cm from the eyes of his friend Ha...
Text Solution
|
- A lens of focal length 5 cm is being used by a student in the laborato...
Text Solution
|
- A myopia person can see things clearly only when they lie between 10 c...
Text Solution
|
- A person wants to read a book placed at 20 cm whereas the near poit of...
Text Solution
|
- The far point of a myopia person is 200 cm. Calculate the power of a l...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the structure and functioning of the human eye. How are we abl...
Text Solution
|
- What is atmospheric refraction ? Use this phenomenon to explain the fo...
Text Solution
|
- What is Tyndall effect? What is its cause ? Name two phenomena observe...
Text Solution
|