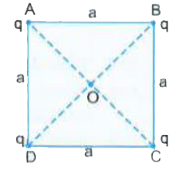
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS|40 VideosELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS|48 VideosELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise TRUE OR FALSE|7 VideosELECTROMAGNETICE INDUCTION
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise Self Assessment Test Section -D|1 VideosEXAMINATION PAPER 2020 (SOLVED)
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SECTION D|6 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
U-LIKE SERIES-ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE -ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS
- Assertion (A): The surface of spherical conductor can be considered as...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A): A bird perches on an electric power line but nothing ha...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A): If the distance between plates of a parallel plate capa...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A): Two equipotential surfaces can never intersect. Reaso...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A): For identical charges of magnitude g each are placed at...
Text Solution
|