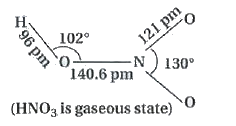
Physical Properties : In a gaseous state, `HNO_(3)` exists as a planar molecule.
It is a colourless liquid (f.p. 231.4 K and b.p. 355.6 K). Laboratory grade nitric acid contains 68% of the `HNO_(3)` by mass and has specific gravity of 1.504.
Chemical properties : In aqueous solution, nitric acid behaves as a strong acid giving hydronium and nitrate ions.
`HNO_(3)(aq) + H_(2)O(l) to H_(3)O_(aq)^(+) + NO_(3)^(-) (aq)`
Concentrated nitric acid is a strong oxidizing agent and attacks most of the metals such as gold and platinum. The products of oxidation depend upon the concentration of the acid, temperature and nature of the material undergoing oxidation.
`3Cu + 8HNO_(3)("dilute")to 3Cu(NO_(3))_(2) + 2NO + 4H_(2)O`
`Cu + 4HNO_(3) ("conc") to Cu(NO_(3))_(2) + 2NO_(2) + 2H_(2)O`
Zinc reacts with dilute nitric acid to give `N_(2)O` and with concentrated acid to give `NO_(2)`
`Zn + 4HNO_(3)("conc") to Zn(NO_(3))_(2) + 2NO_(2) + 2H_(2)O`
Some metals such as Cr, Al etc. do not dissolve in concentrated nitric acid because of the formation of a passive film of oxide on the surface.
Concentrated nitric acid also oxidizes non-metals and their compounds. Iodine is oxidized to iodic acid, carbon to carbon dioxide, sulphur to `H_2SO_(4)` and phosphorus to phosphoric acid.
`I_(2) + 10HNO_(3) to 2HIO_(3) + 10NO_(2) + 4H_(2)O`
`C + 4HNO_(3) to CO_(2) + 2H_(2)O + 4NO_(2)`
`S_(8) + 48HNO_(3) to 8H_(2)SO_(4) + 48NO_(2) + 16H_(2)O`
`P_(4) + 20HNO_(3) to 4H_(3)PO_(4) + 20NO_(2) + 4H_(2)O`
