Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
QUADRILATERALS
RS AGGARWAL|Exercise EXERCISE 10C|18 VideosQUADRILATERALS
RS AGGARWAL|Exercise Multiple Choice Questions (Mcq)|47 VideosQUADRILATERALS
RS AGGARWAL|Exercise Exercise 10 A|10 VideosPROBABILITY
RS AGGARWAL|Exercise Multiple Choice Questions (Mcq)|16 VideosTRIANGLES
RS AGGARWAL|Exercise MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQ)|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RS AGGARWAL-QUADRILATERALS-EXERCISE 10B
- In the adjoining figure, ABCD is a parallelogram in which angle A =72...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjoining figure, ABCD is a paralleogram in which angle DAB=80^...
Text Solution
|
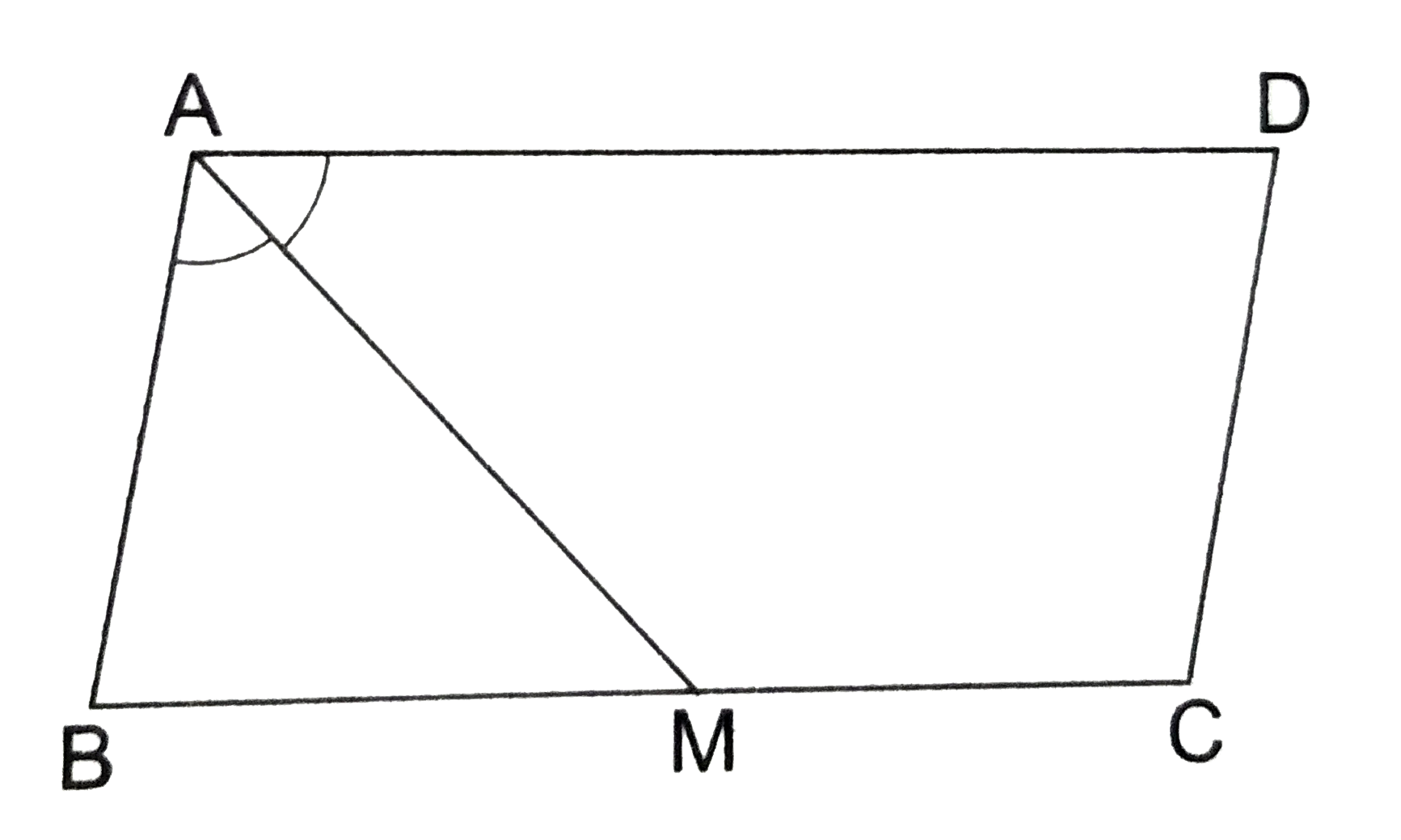
- In the adjoining figure, M is the midpoint of side BC of a paralleogr...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjoining figure, ABCD is a parallelogram in which angle A = ...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjoining figure , ABCD is a parallelogram in which angle BAO=...
Text Solution
|
- In a parallelogram ABCD , if /A=(2x+25)^@ and /B=(3x-5)^@. Find the va...
Text Solution
|
- If an angle of a parallelogram is four fifths of its adjacent angle, f...
Text Solution
|
- Find the measure of each angle of a parallelogram, if one of its angle...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is a parallelogram in which AB=9.5 cm and its perimeter is 30 c. ...
Text Solution
|
- In each of the figures given below, ABCD is a rhombus. Find the value...
Text Solution
|
- The length of the diagonals of a rhombus are 24cm and 18cm respectivel...
Text Solution
|
- Each side of a rhombus is 10 cm long and one of its diagonals measures...
Text Solution
|
- In each of the figures given below, ABCD is a rectangle. Find the valu...
Text Solution
|
- A B C D is a rhombus in which the altitude from D to side A B\ bisect...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjoining figure, ABCD is a square. A line segment CX cuts AB a...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is a rhombus. Show that diagonal AC bisects /Aas well as /Cand d...
Text Solution
|
- In a parallelogram ABCD, points M and N have been taken on opposite si...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjoining figure, ABCD is a parallelogram.If P and Q are the ...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjoining figure, ABCD is a parallelogram whose diagonals int...
Text Solution
|
- The angle between the altitudes of a parallelogram, through the sam...
Text Solution
|