Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section - B (Numericals) Numerical From Textual Illustration|8 VideosTHERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section - B|10 VideosTHERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Try Yourself (VSQs)|84 VideosSYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-F (SECTION-D) QUESTIONS PAPER|1 VideosTHERMODYANMICS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Question Paper|11 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER-Information : Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS)
- What is the triple point ?
Text Solution
|
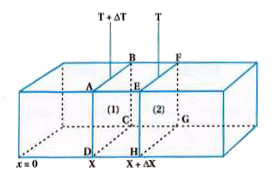
- Derive equation for heat flow rate in rectangular block of solid.
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the factors on which amount of thermal energy passing perpendi...
Text Solution
|
- Derive equation for heat flow rate in rectangular block of solid.
Text Solution
|
- Explain thermal resistance.
Text Solution
|
- What is perfect black body ? Give examples.
Text Solution
|
- Explain cavity and cavity radiation.
Text Solution
|
- Why Sun is considered as perfect black body ? Explain and also Explain...
Text Solution
|