Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section - B|10 VideosTHERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section - B (Numericals) Numerical From Textual Exercise|26 VideosTHERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Information : Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS)|8 VideosSYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-F (SECTION-D) QUESTIONS PAPER|1 VideosTHERMODYANMICS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Question Paper|11 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER-Section - B (Numericals) Numerical From Textual Illustration
- Show that the coefficient of area expansions, (DeltaA//A)//DeltaT, of ...
Text Solution
|
- A blacksmith fixes iron ring on the rim of the wooden wheel of a bullo...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of aluminium of 0.047 kg placed for sufficient time in a vess...
Text Solution
|
- When 0.15 kg of ice of "0 "^(@)C mixed with 0.30 kg of water at "50 "^...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the heat required to convert 3 kg of ice at -12" "^(@)C kept...
Text Solution
|
- What is the temperature of the steel-copper junction is the steady sta...
Text Solution
|
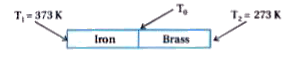
- An iron bar (L(1)=0.1" m",A(1)=0.02" m"^(2),K(1)=97" Wm"^(-1)K^(-1)) a...
Text Solution
|
- A pan filled with hot food cools from 94^(@)C to 86^(@)C in 2 minutes ...
Text Solution
|