Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
LAW OF MOTION
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION -B (ADDITIONAL EXERCISE )|17 VideosLAW OF MOTION
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION -B (NUMERICAL FROM DARPAN BASED ON TEXTBOOK)|8 VideosLAW OF MOTION
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION -B (NUMERICAL FROM TEXTUAL ILLUSTRATION)|12 VideosGRAVITATION
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise QUESTIONS PAPER Section - D|1 VideosMACHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise QUESTION PAPER|11 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-LAW OF MOTION-SECTION -B (NUMERICAL FROM TEXTUAL EXERCISE)
- One end of a string of length l is connected to a particle of mass m a...
Text Solution
|
- A constant retarding force of 50 N is applied to a body of mass 20 kg ...
Text Solution
|
- A constant force acting on a body of mass 3.0 kg changes its speed fro...
Text Solution
|
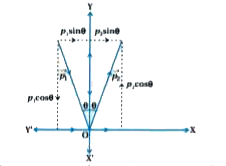
- A body of mass 5 kg is acted upon by two perpendicular forces 8 N and ...
Text Solution
|
- The driver of a three-wheeler moving with a speed of 36 km/h sees a ch...
Text Solution
|
- A rocket with a lift-off mass 20,000 kg is blasted upwards with an ini...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 0.40 kg moving initially with a constant speed of 10 m ...
Text Solution
|
- A truck starts from rest and accelerates uniformly at 2.0 m s^(-2). A...
Text Solution
|
- A bob of mass 0.1 kg hung from the ceiling of a room by a string 2 m l...
Text Solution
|
- A man of mass 70 kg stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is movi...
Text Solution
|
- Shows the position-time graph of a particle of mass 4 kg. What is the ...
Text Solution
|
- Two bodies of m asses 10 kg and 20 kg respectively kept on a smooth, h...
Text Solution
|
- Two masses 8 kg and 12 kg are connected at the two ends of a light ine...
Text Solution
|
- A nucleus is at rest in the laboratory frame of reference. Show that i...
Text Solution
|
- Two billiard balls each of mass 0.05 kg moving in opposite directions ...
Text Solution
|
- A shell of mass 0.020 kg is fired by a gun of mass 100 kg. If the muz...
Text Solution
|
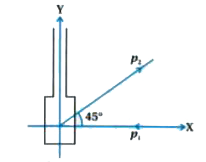
- A batsman deflects a ball by an angle of 45^(@) without changing its i...
Text Solution
|
- A stone of mass 0.25 kg tied to the end of a string is whirled round i...
Text Solution
|
- If, in , the speed of the stone is increased beyond the maximum permis...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why (a) a horse cannot pull a cart and run in empty space, ...
Text Solution
|