Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS : MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section-B : Numericals (Numerical From Textual illustrations)|16 VideosSEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS : MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section-B : Numericals (Numerical From Textual Exercise)|15 VideosSEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS : MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section-D : Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) (MCQs asked in Competitive Exams)|129 VideosSAMPLE QUESTION PAPER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise PART-B SECTION-C|5 VideosWAVE OPTICS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-D (MULTIPLCE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQS)) (MCQS FROM DARPAN BASED ON TEXTBOOK)|239 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-SEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS : MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS -Section-A : Questions - Answers
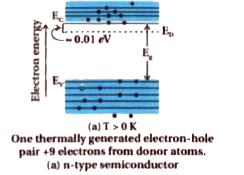
- What is n-type semiconductor? Name the majority and minority carriers ...
Text Solution
|
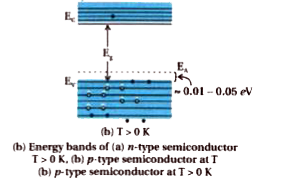
- What is p-type semiconductor? Name the majority and minority carriers ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain n and p-type semiconductor based on band theory.
Text Solution
|
- Explain recombination coefficient of intrinsic semiconductor and obtai...
Text Solution
|
- Write four points in distinguishing between p-type semiconductor and n...
Text Solution
|
- Write the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductor.
Text Solution
|
- Which is the primary constitutional unit for diode and transistor?
Text Solution
|
- How p-n junction diode is formed ? And explain depletion layer and bar...
Text Solution
|
- What is depletion barrier?
Text Solution
|
- Write short on semiconductor diode.
Text Solution
|
- State the methods of connection of p-n junction.
Text Solution
|
- What is forward bias and reverse bias ?
Text Solution
|
- When is the p-n junction called reverse bias and explain the change in...
Text Solution
|
- What is static characteristic of p-n junction and write its types.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the forward characteristics of the p-n junction diode by drawi...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the reverse characteristics of p-n junction diode by circuit d...
Text Solution
|
- What is rectification and rectifier ? Why p-n junction diode is used a...
Text Solution
|
- Write the principle of rectifier.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the use of the junction diode as a half wave rectifier by draw...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the use of junction diode as a full wave rectifier by drawing ...
Text Solution
|