Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS : MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section-B : Numericals (Numerical From Textual illustrations)|16 VideosSEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS : MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section-B : Numericals (Numerical From Textual Exercise)|15 VideosSEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS : MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section-D : Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) (MCQs asked in Competitive Exams)|129 VideosSAMPLE QUESTION PAPER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise PART-B SECTION-C|5 VideosWAVE OPTICS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-D (MULTIPLCE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQS)) (MCQS FROM DARPAN BASED ON TEXTBOOK)|239 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-SEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS : MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS -Section-A : Questions - Answers
- What is rectification and rectifier ? Why p-n junction diode is used a...
Text Solution
|
- Write the principle of rectifier.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the use of the junction diode as a half wave rectifier by draw...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the use of junction diode as a full wave rectifier by drawing ...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the simple filter circuit for obtaining smooth rectified volt...
Text Solution
|
- Write short note on zener diode.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the use of Zener diode as a voltage regulator.
Text Solution
|
- What are optoelectronic devices? Give the names of such major devices.
Text Solution
|
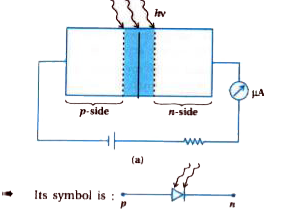
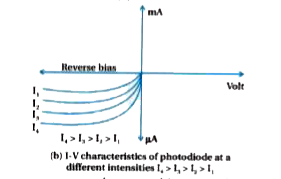
- Explain construction and working of photodiode.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the design, working, uses and benefits of light emitting diode...
Text Solution
|
- Describe construction, working and use of the solar cell.
Text Solution
|
- What are the ideal materials for fabrication of solar cell? and give t...
Text Solution
|
- What is digital signal ? What mathematical method are expressed in it?
Text Solution
|
- write types of logic system.
Text Solution
|
- What is logic gate?
Text Solution
|
- Write the symbol, truth table, function and Boolean equation for NOT g...
Text Solution
|
- Write the symbol, truth table, function and Boolean equation for OR g...
Text Solution
|
- Write the symbol, truth table, function and Boolean equation for AND g...
Text Solution
|
- What is NAND gate? Write its symbol, truth table and Boolean equation.
Text Solution
|
- What is NOR gate? Write its symbol, truth table and Boolean equation.
Text Solution
|