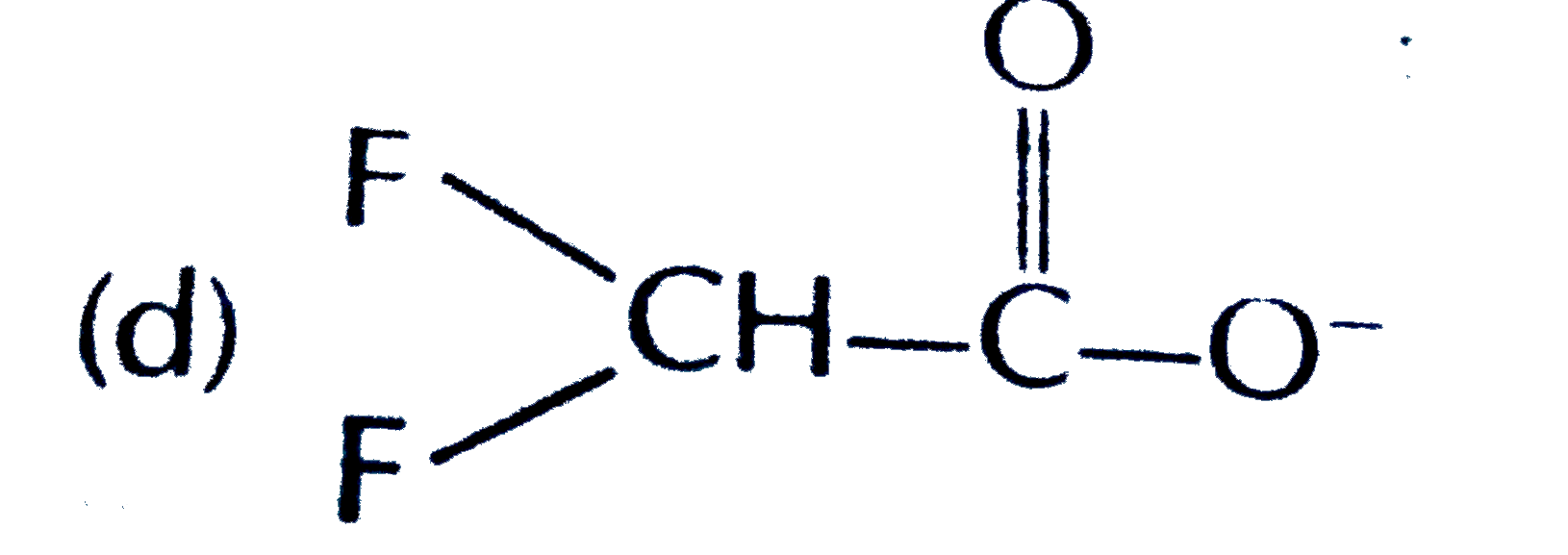
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Short Answer type question|27 VideosORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Matching the columns|5 VideosHYDROGEN
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS|8 VideosREDOX REACTIONS
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS|6 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH-ORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES-Long Answer type question
- Ionic species are stailised by the dispersal of charge. Which of the f...
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by hybridisation ? Compound CH(2)=C=CH(2) contains sp or...
Text Solution
|
- Benzoic acid is an organic compound. Its crude sample can be purified ...
Text Solution
|
- Two liquids (A) and (B) can be separated by the method of fractional d...
Text Solution
|
- You have a mixture of three liquids A, B and C. There is a large diffe...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a diagram of bubble plate type fractionating column. When do we r...
Text Solution
|
- A liquid with high boiling point decomposes on simple distillation but...
Text Solution
|