Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CIRCLES
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 10.3|20 VideosCIRCLES
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 10.4|14 VideosCIRCLES
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 10.4|14 VideosAreas of Parallelograms and Triangles
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-9.4 Long Answer Type Questions|10 VideosCONSTRUCTIONS
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Long Answer Type Questions|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH-CIRCLES-Exercise 10.2
- Two chords AB and CD of a circle are each at distances 4 cm from the c...
Text Solution
|
- Two chords AB and AC of a circle with centre O are on the opposite sid...
Text Solution
|
- The congruent circles with centres Oand O' intersect at two points A a...
Text Solution
|
- Through three collinear points a circle can be draw.
Text Solution
|
- A circle of radius 3 cm can be drawn through two points A, B such that...
Text Solution
|
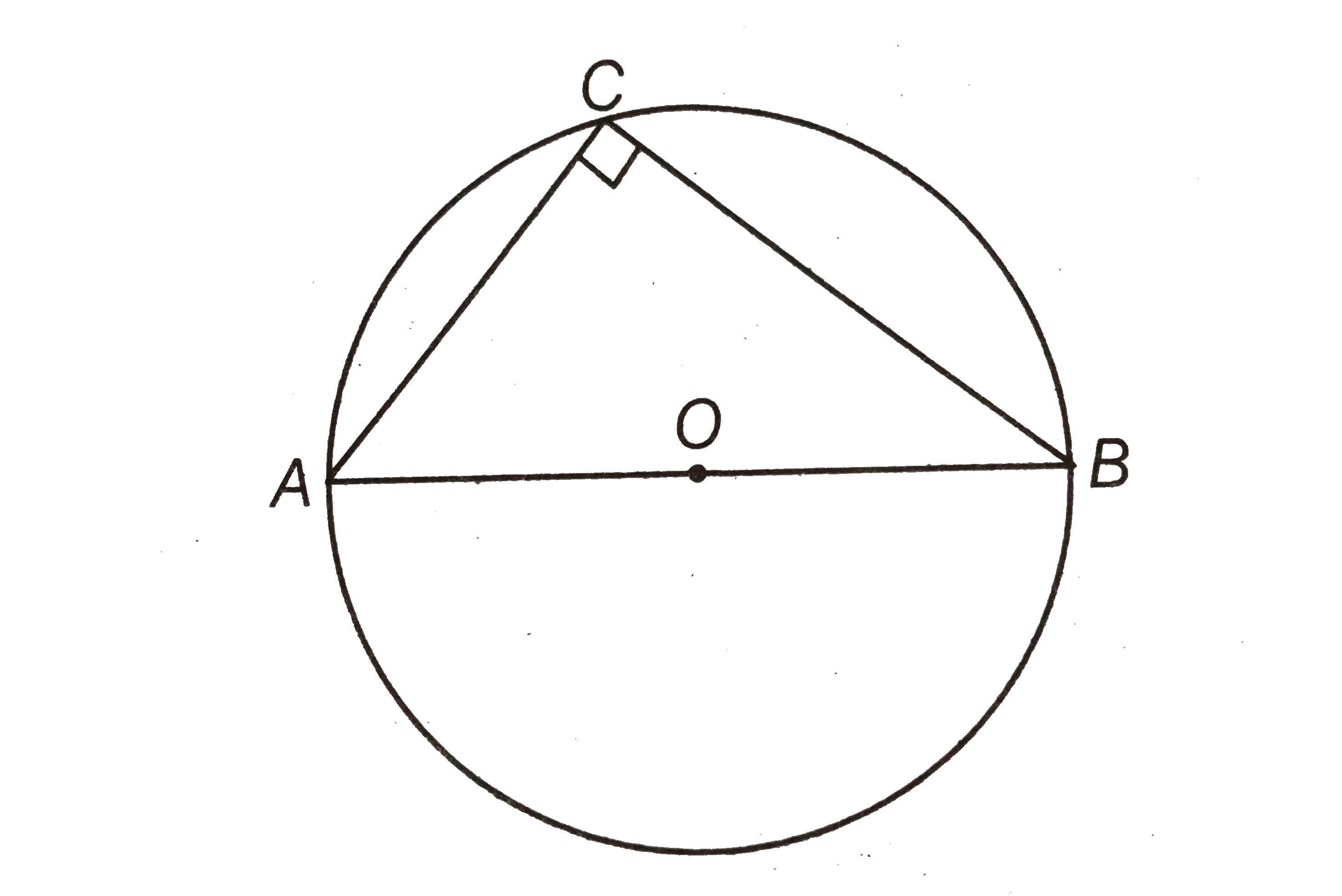
- If AOB is a diameter of a circle and C is a point on the circle, then ...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral such that angleA=90^(@),angleB=70^(@),a...
Text Solution
|
- If A, B, C and D are four points such that angleBAC=30^(@)and angleBDC...
Text Solution
|
- If A, B, C and D are four points such that angleBAC=45^(@) and angleBD...
Text Solution
|
- In figure, if AOB is a diameter and angleADC=120^(@),"then"angleCAB=30...
Text Solution
|