A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH-WAVE OPTICS-Long Answer type Questions
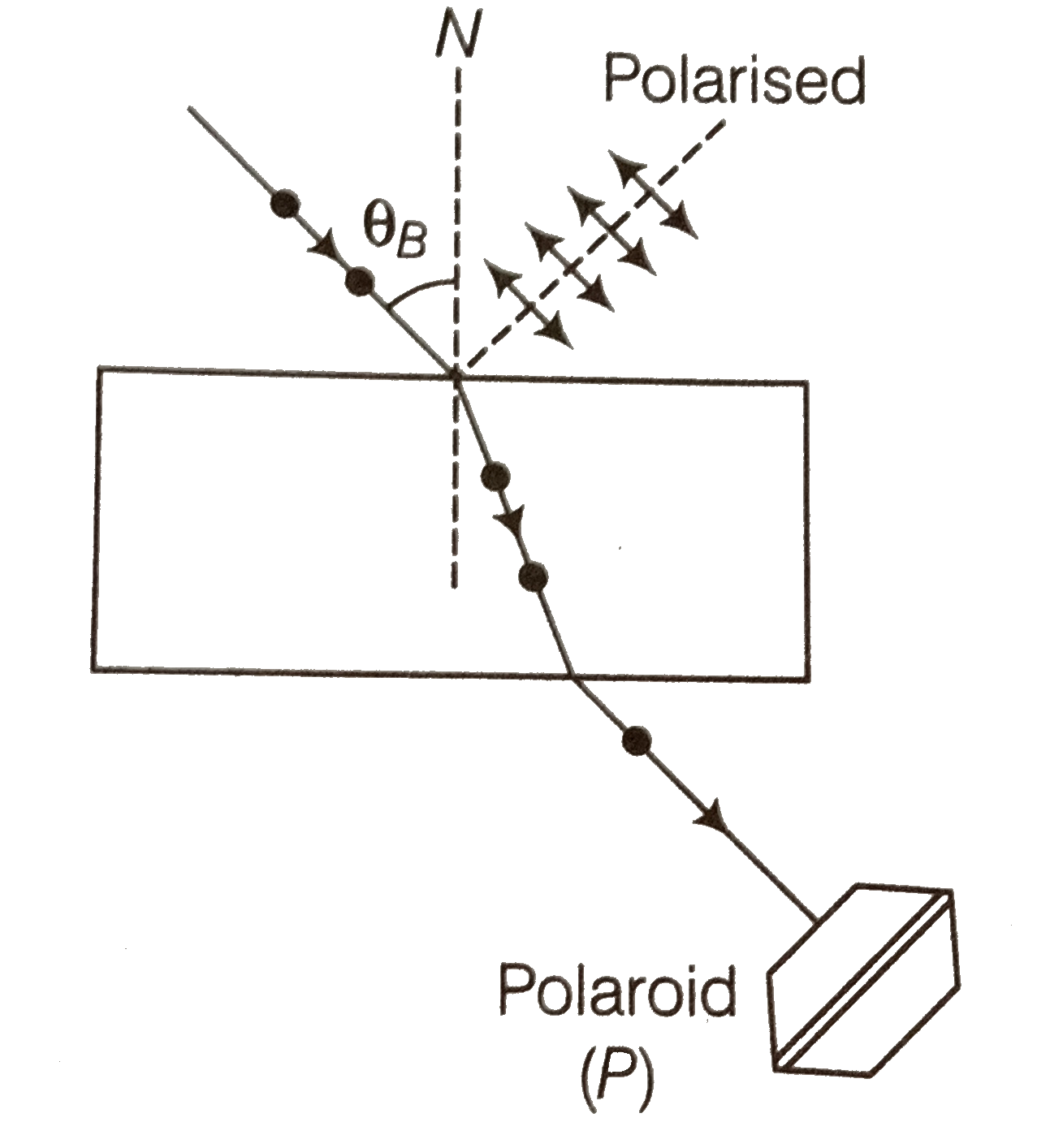
- Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster's ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shown a two slit arrangement with a source which emits unpolar...
Text Solution
|
- A small transparent slab containing material of mu=1.5 is placed along...
Text Solution
|
- Four identical monochromatic sources A,B,C,D as shown in the (figure) ...
Text Solution
|
- The optical properties of a medium are governed by the relative permit...
Text Solution
|
- To ensure almost 100% transmittivity, photographic lenses are often co...
Text Solution
|