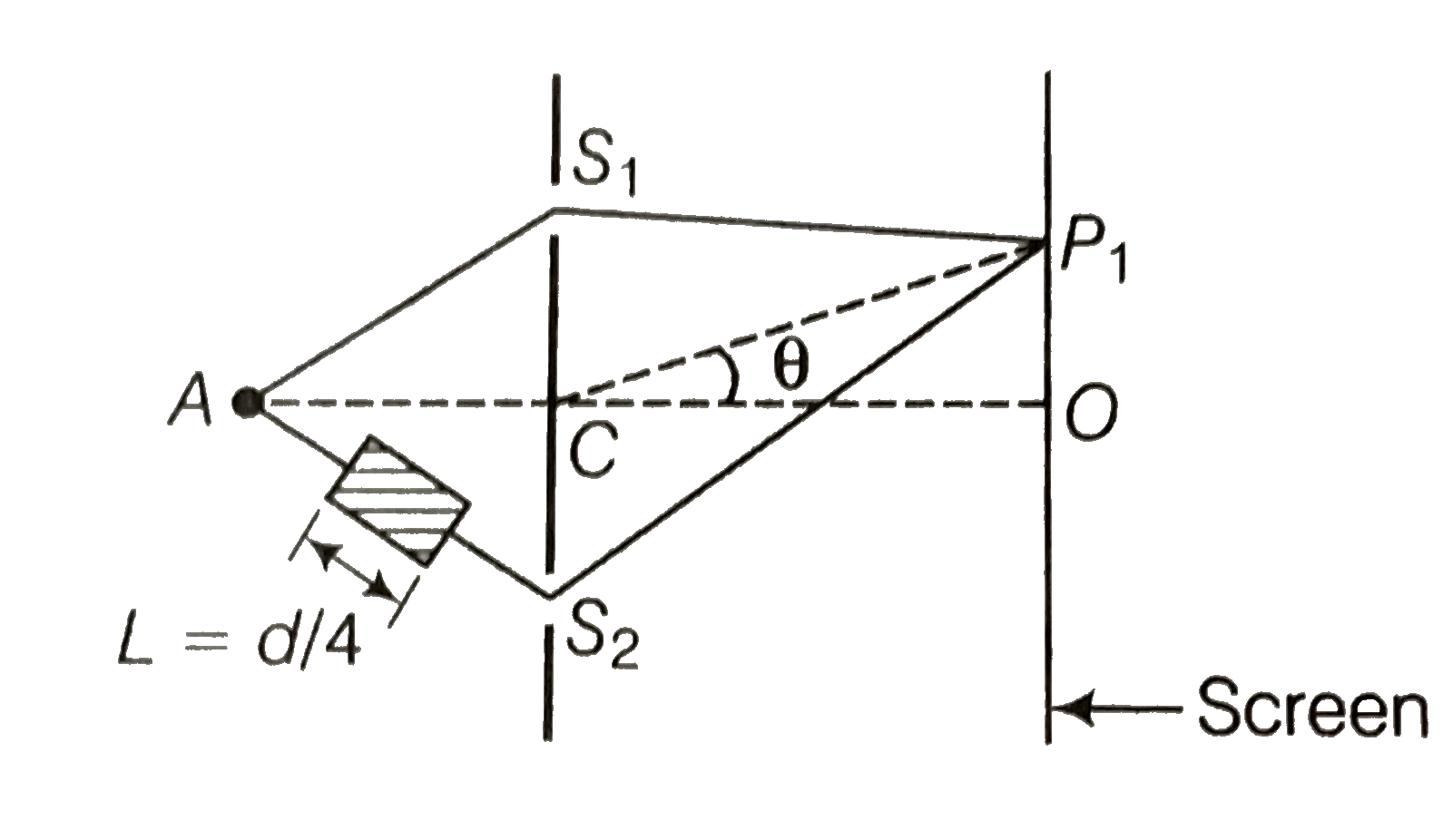
A small transparent slab containing material of `mu=1.5` is placed along `AS_(2)`(figure). What will be the distance from O of the principle maxima and of the first minima on either side of the principal maxima obtained in the absence of the glass slab ?

A small transparent slab containing material of `mu=1.5` is placed along `AS_(2)`(figure). What will be the distance from O of the principle maxima and of the first minima on either side of the principal maxima obtained in the absence of the glass slab ?
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
In case of transparent glass slabe of refractive indesx `mu`, the path difference will be calculated as `Deltax=2d sin theta+(mu-1)L`
In case of transparent glass slab of refractive index `mu`,
the path difference `=2d sin theta + (mu-1)L.`
For the principal maxima, (path difference is zero )
i.e., ` 2d sin theta _(0)+(mu-1)L=0`
or, `sin theta_(0)= -(L(mu-1))/(2d)=(-L(0.5))/(2d)" " [:. L=d//4]`
or `sin theta_(0)=(-6)/(16)`
`:. OP=D tan theta_(0)~~D sin theta_(0)=(-D)/(16)`
For the first minima, the path difference is `pm(lambda)/(2)`
`:. 2d sin theta_(1)+0.5L = pm(lambda)/(2)`
or `sin theta_(1)=(pm lambda//2 -0.5L)/(2d)=(pm lambda//2-d//8)/(2d)`
`=(pm lambda//2- lambda//8)/(2 lambda)=pm(1)/(4)-(1)/(16)`
[`:.` The diffraction occurs if the wavelength of waves in nearly equal to the side width (d)]
On the positive side `sin theta'_(1)^(+)= +(1)/(4)-(1)/(16)=(3)/(16)`
On the negative side `sin theta''_(1)^(-)=-(1)/(4)-(1)/(16)=-(5)/(16)`
The First principal maxima on the positive side is at distance
`D tan theta'_(1)^(+)=D ( sin theta'_(1)^(+))/(sqrt(1- sin^(2) theta'_(1)))=D(3)/(sqrt(16^(2)-3^(2)))=(3D)/(sqrt(247))` above point O
The first principal minima on the negative side is at distance
`D tan theta''_(1)=(5D)/(sqrt(16^(2)-5^(2))=(5D)/(sqrt(231))` below point O.
In case of transparent glass slab of refractive index `mu`,
the path difference `=2d sin theta + (mu-1)L.`
For the principal maxima, (path difference is zero )
i.e., ` 2d sin theta _(0)+(mu-1)L=0`
or, `sin theta_(0)= -(L(mu-1))/(2d)=(-L(0.5))/(2d)" " [:. L=d//4]`
or `sin theta_(0)=(-6)/(16)`
`:. OP=D tan theta_(0)~~D sin theta_(0)=(-D)/(16)`
For the first minima, the path difference is `pm(lambda)/(2)`
`:. 2d sin theta_(1)+0.5L = pm(lambda)/(2)`
or `sin theta_(1)=(pm lambda//2 -0.5L)/(2d)=(pm lambda//2-d//8)/(2d)`
`=(pm lambda//2- lambda//8)/(2 lambda)=pm(1)/(4)-(1)/(16)`
[`:.` The diffraction occurs if the wavelength of waves in nearly equal to the side width (d)]
On the positive side `sin theta'_(1)^(+)= +(1)/(4)-(1)/(16)=(3)/(16)`
On the negative side `sin theta''_(1)^(-)=-(1)/(4)-(1)/(16)=-(5)/(16)`
The First principal maxima on the positive side is at distance
`D tan theta'_(1)^(+)=D ( sin theta'_(1)^(+))/(sqrt(1- sin^(2) theta'_(1)))=D(3)/(sqrt(16^(2)-3^(2)))=(3D)/(sqrt(247))` above point O
The first principal minima on the negative side is at distance
`D tan theta''_(1)=(5D)/(sqrt(16^(2)-5^(2))=(5D)/(sqrt(231))` below point O.
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Light of wavelength 6 xx10^(-5) cm falls on screen at a distance of 100 cm from a narrow slit. Find the width of the slit if the first minima lies 1mm on either side of the central maximum
Light of wavelength lambda = 500 nm falls on two narrow slits placed a distance d = 50 xx 10^-4 cm apart, at an angle phi= 30^@ relative to the slits as shown in figure. On the lower slit a transparent slab of thickness 0.1 mm and refractive index 3/2 is placed. The interference pattern is observed at a distance D=2m from the slits. Then, calculate (a) position of the central maxima. (b) the order of maxima at point C of screen . (c)how many fringes will pass C, if we remove the transparent slab from the lower slit?
A biconvex thin lens of radius of curvature R is made up of variable refractive index mu=2(1+r/d) . Assume 2d lt lt R . There are infinite images of the point O, which is placed at a distance R on the principal axis from the lens as shown in the figure. The image is spread along the pricipal axis in a length of (r is the radial distance from P measured perpendicular to principal axis)
In YDSE arrangement as shown in figure, fringes are seen on screen using monochromatic source S having wavelength 3000 Å (in air). S_1 and S_2 are two slits seperated by d = 1 mm and D = 1m. Left of slits S_1 and S_2 medium of refractive index n_1 = 2 is present and to the right of S_1 and S_2 medium of n_2 = 3/2 , is present. A thin slab of thickness 't' is placed in front of S_1 . The refractive index of n_3 of the slab varies with distance from it's starting face as shown in figure. In order to get central maxima at the centre of screen, the thickness of slab required is :
An object is placed 21 cm in fron of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 20 cm.A glass slab of thicknes 3 cm and refractive index 1.5 is palced close to the mirror in the space between the object and the mirror. Find the position of the final image fromed. The distance of the nearer surface of the slab from the mirror is 10 cm.
In Young's double-slit experiment, a point source is placed on a solid slab of refractive index 6//5 at a distance of 2 mm from two slits spaced 3 mm apart as shown and at equal distacne from both the slits. The screen is at a distance of 1 m from the slits. Wavelength of light used is 500 nm. a. Find the position of the central maximum. b. Find the order of the fringe formed at O. c. A film of refractive index 1.8 is to be placed in front of S_(1) so that central maxima is formed where 200th maxima was formed. Find the thickness of film.
A transparent cube contains a small air bubble. Its apparent distance is 2 cm when seen through other facel. If the refractive index of the material of the cube is 1.5, the real length of the edge of cube must be
A point object is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens (f = 15 cm) at a distance of 30 cm from it. A glass plate (mu= 1.50) of thickness 1 cm is placed on the other side of the lens perpendicular to the axis. Locate the image of the point object.
The figure ,shows a transparent sphere of radius R and refractive index mu .An object O is placed at a distance x from the pole of the first surface so that a real image is formed at the pole of the exactly opposite surface. if an object is Placed at a distance R from the pole of first surface ,then the real image is formed at a distance R from thepole of the second surface.The refractive index mu of the spher is given by
A monochromatic light of lambda=500 nm is incident on two identical slits separated by a distance of 5xx10^(-4)m . The interference pattern is seen on a screen placed at a distance of 1 m from the plane of slits. A thin glass plate of thickness 1.5xx10^(-6)m and refractive index mu=1.5 is placed between one of the slits and the screen. Find the intensity at the center of the screen if the intensity is I_(0) in the absence of the plate. Also find the lateral shift of the central maxima and number of fringes crossed through center.
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH-WAVE OPTICS-Long Answer type Questions
- Figure shown a two slit arrangement with a source which emits unpolar...
Text Solution
|
- A small transparent slab containing material of mu=1.5 is placed along...
Text Solution
|
- Four identical monochromatic sources A,B,C,D as shown in the (figure) ...
Text Solution
|
- The optical properties of a medium are governed by the relative permit...
Text Solution
|
- To ensure almost 100% transmittivity, photographic lenses are often co...
Text Solution
|