To solve the problem of determining the velocity of a pebble dropped into a viscous fluid (oil) as a function of time, we can follow these steps:
### Step 1: Understand the Forces Acting on the Pebble
When the pebble is dropped, three main forces act on it:
1. **Gravitational Force (Weight)**: This force acts downward and is constant, given by \( F_g = mg \).
2. **Buoyant Force**: This acts upward and is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the pebble, given by \( F_b = \rho_f V g \), where \( \rho_f \) is the density of the fluid, \( V \) is the volume of the pebble, and \( g \) is the acceleration due to gravity.
3. **Viscous Drag Force**: This force opposes the motion of the pebble and increases with velocity, given by \( F_d = 6 \pi \eta r v \), where \( \eta \) is the viscosity of the fluid, \( r \) is the radius of the pebble, and \( v \) is the velocity of the pebble.
### Step 2: Analyze the Motion of the Pebble
Initially, when the pebble is dropped, it has zero velocity. As it falls, the gravitational force causes it to accelerate downward. However, as the velocity increases, the viscous drag force also increases, opposing the motion.
### Step 3: Determine the Terminal Velocity
Eventually, the pebble will reach a point where the net force acting on it becomes zero. This occurs when the downward gravitational force is balanced by the upward buoyant force and the viscous drag force. At this point, the pebble reaches its terminal velocity \( v_t \):
\[ mg = F_b + F_d \]
At terminal velocity, the acceleration becomes zero, and the velocity remains constant.
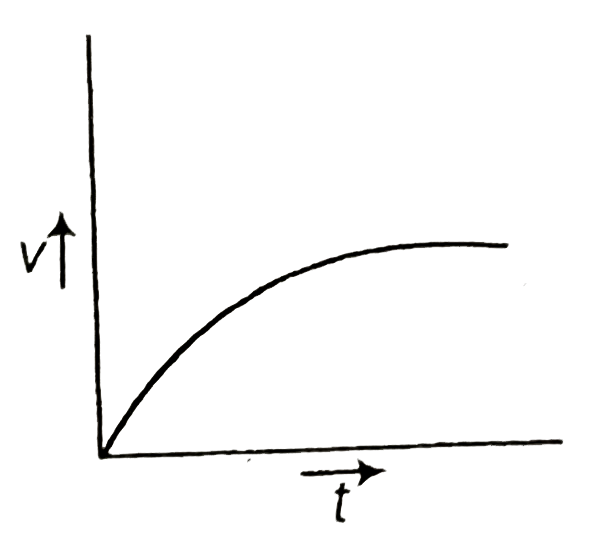
### Step 4: Sketch the Velocity vs. Time Graph
1. **Initial Phase**: The pebble starts from rest (velocity = 0) and begins to accelerate downward. The velocity increases rapidly at first.
2. **Decreasing Acceleration**: As the pebble continues to fall, the acceleration decreases because the viscous drag force increases with velocity.
3. **Terminal Velocity**: Eventually, the pebble reaches a constant terminal velocity where the velocity no longer increases, and the graph levels off.
### Step 5: Identify the Correct Graph
From the description of the motion:
- The graph should start at the origin (0,0) since the initial velocity is zero.
- It should show a curve that rises steeply at first (indicating increasing velocity) and then levels off as it approaches terminal velocity.
### Conclusion
The graph that represents the velocity of the pebble as a function of time will show a curve that starts at zero, rises quickly, and then flattens out as it approaches terminal velocity.