`"Required area, "A=overset(37)underset(1)intg(x)dx=overset(37)underset(1)intf^(-1)(x)dx.`
`"Let "f^(-1)(x)=t or x=f(t)`
Using intelligent gusessing, `f(3)=37 and f(0)=1`
`therefore" "A=overset(3)underset(0)inttf'(t)dt=[tf(t)]_(0)^(3)-overset(3)underset(0)intf(t)dt`
`=3f(3)-overset(3)underset(0)int(t^(3)+3t+1)dt`
`=111-(147)/(4)=(297)/(4)`
Alternative method :
`f(x)=x^(3)+3x+1.`
`therefore" "f'(x)=3x^(2)+3gt0, AA in R.`
`therefore" "f(x)` is an increasing function.
Also, `x^(3)+3x+1=x or x^(3)+2x+1=0` has no positive root.
So, line y=x never meet curve `y=f(x)" for "xgt0`.
Graph of `y=f(x) and y=f^(-1)(x)` are as shown in the following figure.
`"When "y=1,x^(3)+3x+1=1,x=0.`
`"When "y=37, x^(3)+3x=36, x=3`
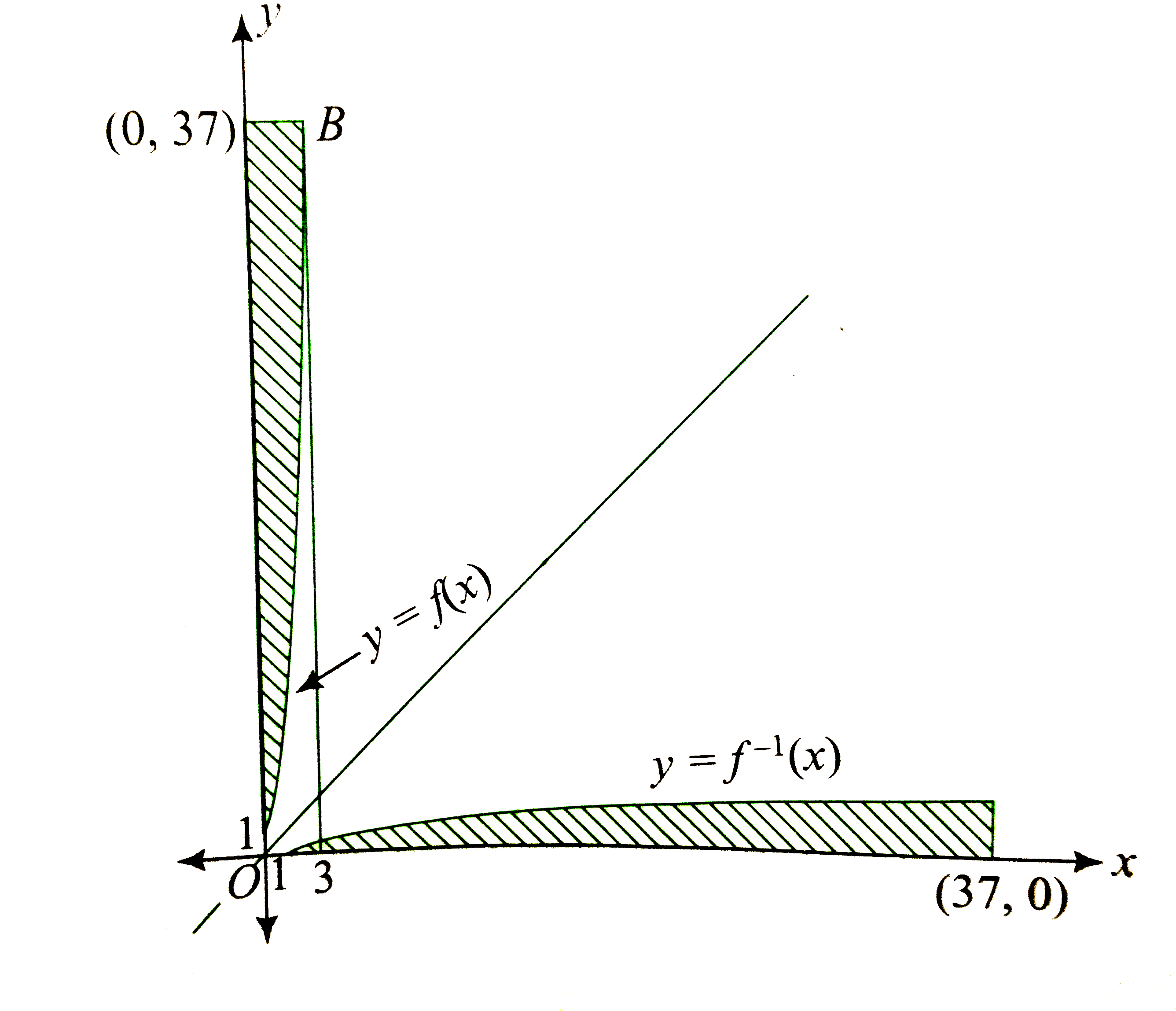
Area bounded by curves `y=f^(-1)(x),` x-axis, x=1 and x=37 is same as area bounded by curves `y=f(x),y`-axis, `y=1 and y=37`.
`therefore" Required area ="overset(3)underset(0)int(37-x^(3)-3x-1)dx`
`=[36x-(x^(4))/(4)-(3x^(2))/(2)]_(0)^(3)=(297)/(4)` sq. units.